

P20 tool steel is a low alloy, chrome-moly steel commonly employed to build mold steels for manufacturing plastic parts. Its excellent polished finish, good weldability, machinability, toughness, and nitriding properties make it a great choice for mold manufacturers.
It is crucial to understand the various properties and attributes of the steel to select the most apt material for your mold application. In this article, we discuss the various characteristics of AISI P20 Tool Steel and its role in manufacturing.
P20 tool steel is a low alloy steel that’s characterized by good toughness at moderate strength levels and excellent dimensional stability during heat treatment. It’s also referred to as chrome-moly alloy steel which is abbreviated for Chromium-Molybdenum.
P20 mold steel is extremely versatile and apt for specific applications. P20 tool steel is a type of tool steel that’s mostly associated with injection mold and tool steels. It’s commonly employed and is considered to be the standard mold steel for plastic injection mold tooling and cavities and zinc die-casting dies in the manufacturing industry.
It’s typically available in the pre-hardened condition of 31-32 HRC. In the case of AISI P20 tool steel, it’s possible to achieve various levels of hardness through additional heat treatment. You should note that it provides unified hardness across wide sections.
When P20 mold steel is prehardened, it can be nitrided for greater wear resistance. In the prehardened state, it can also be textured.
Prehardened P20 is employed for plastic molding and cavities and cores of zinc die-casting dies. It’s also employed for mold parts, in which a high surface hardness isn’t a priority.
P20 mold steel demonstrates easy machinability at 65%. This factor makes it easier to work with during mold manufacturing.
P20 tool steel demonstrates excellent dimensional stability under heat treatment. Thus, P20 is commonly employed for molds. It’s ideal for large plastic molds and die-casting dies.
P20 tool steel offers good polishability, which is a crucial attribute for mold application.
P20 can be polished to a high surface finish, which is necessary for achieving a smooth finish on the plastic parts. It thus makes P20 steel a preferred and suitable choice.
It’s easier to weld mold steel. It provides flexibility during mold design and building.
P 20 is a popularly employed steel. Mold makers are generally familiar with the characteristics and attributes of the P 20 steel. They are also familiar with the heat treatment processes of P 20 mold steel. Since it’s also very versatile, it can be applied to a range of molding applications.
Though P20 tool steel can be hardened, it’s not possible or difficult to achieve the same level of hardness as some other mold steels. With P 20 tool steel, you can go up to 50 to 60 HRC but you should note that the steel needs to be processed well to reach those levels of hardness. Since the steel hardness is limited, it impacts wear resistance in certain applications.
P 20 mold steel has a low corrosion resistance. It rusts easily as it doesn’t contain chromium or other corrosion-resistant elements. You should note that it’s not stainless steel thus, it requires correct maintenance to avoid corrosion.
Mold steel is named by AISI, abbreviated for the American Iron and Steel Institute, and SAE, abbreviated for the Society of Automotive Engineers in the United States.
AISI and SAE together have developed UNS, abbreviated for Unified Numbering System. UNS is a steel grade numbering system and the UNS for P 20 Tool Steel is UNS T51620.
AISI classification system denoted the letter ‘P’ to categorize a particular set of mold steels i.e. ‘Group P’ steels. All steels that are designated with the letter P are low alloy steels and the main alloying elements in these mold steels are chromium and nickel.
The P group of steels includes mold steels such as P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P20, and P21 steels.

P20 tool steel is a low alloy steel. It has similar grades, available internationally. These grades are not exactly P 20 steel but they are similar in element and composition. It is thus crucial to comply with the country’s standards. The equivalent grades of AISI P20 tool steel in Germany and China are listed below:

P20 tool steel is one of the most widely employed steels from the Cr-Mo series! It’s a pre-hardened tool steel with good physical properties such as high strength and excellent durability.
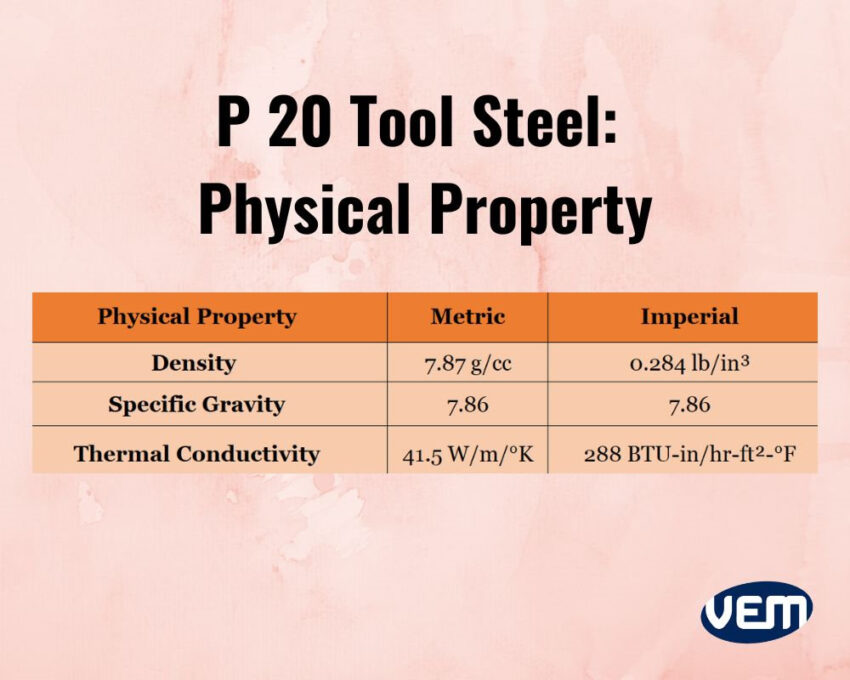
AISI P20 tool steel demonstrates good polishability and is easily machinable thus, enabling the manufacturers to shape the steel easily. You should note that the steel’s cold-forming performance enables flexibility in manufacturing.
It also exhibits excellent weldability, and ductility thus, ensuring that it can be deformed without breaking.
P20 tool steel in hardened and tempered condition is ready for machining. In its hardened condition, it demonstrates excellent wear resistance. It’s typically hardened up to 31 HRC. It can be directly processed without heat treatment and it demonstrates uniform hardness.
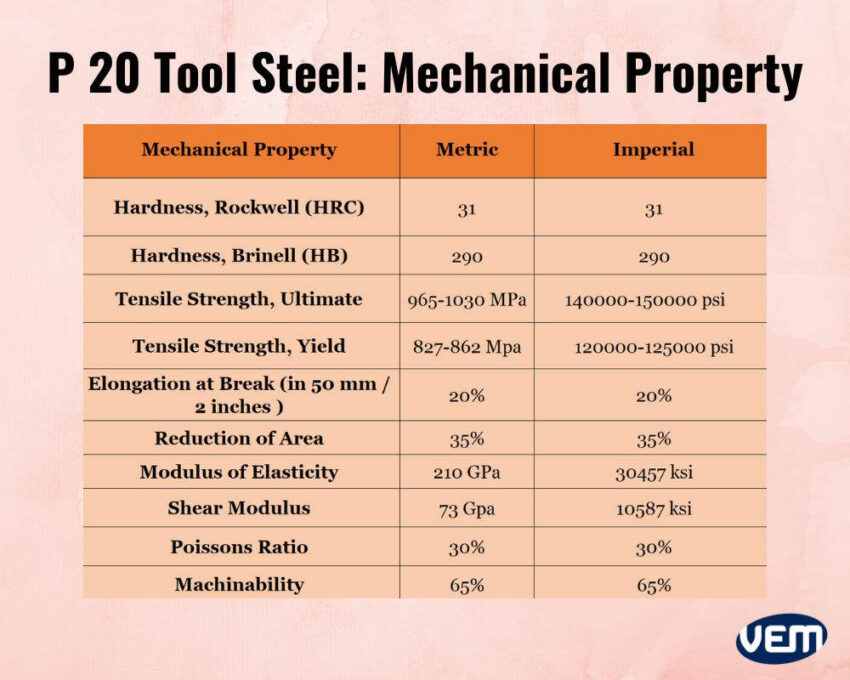
P20 tool steel is a low alloy steel. The chemical composition of AISI P20 tool steel consists of 0.28 to 0.40% Carbon along with 1.8 to 2.1% Chromium, 0.15 to 0.35% Molybdenum, 1.3 to 1.6% Manganese, and 0.2 to 0.4% Silicon. This chemical composition of P 20 tool steel imparts it with excellent wear resistance and high ductility.
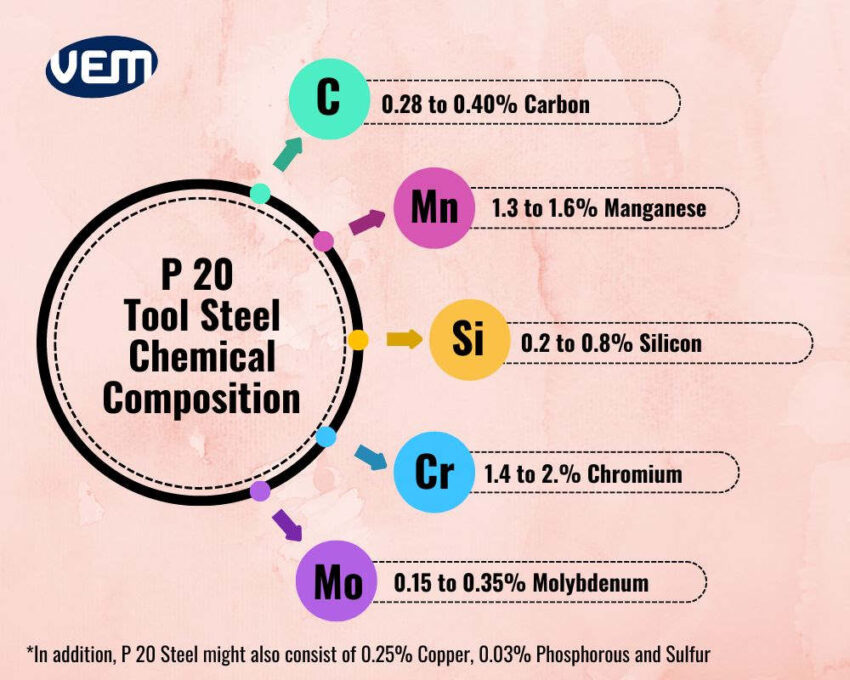
The Carbon content of the P 20 steel is between 0.28 to 0.4%. It’s a low alloy and low-carbon mold steel.
The Manganese imparts the steel with tensile strength and hardenability just like Carbon does. In addition, it also helps to remove various impurities such as oxygen and sulfur from the molten steel.
Silicon strengthens the alloy’s iron and it also boosts its hardness. In addition, it also helps to remove oxygen impurities and bubbles from the molten steel, just like Manganese.
The chromium content in the P 20 steel is approximately between 1.4 to 2%. It helps to increase the hardness and the toughness of the steel.
Molybdenum improves the corrosion resistance of the P20 tool steel. It also increases the creep strength in high temperatures and hardenability.
Copper in AISI P20 tool steel aids with the corrosion resistance of the P20 tool steel. In addition, it also helps to increase the hardenability of the steel.
Phosphorus is present in a very tiny amount of 0.03% and is generally considered an impurity in steel. It does help to increase the corrosion resistance and strength of the steel but it’s crucial to limit the phosphorus content as too much of it can cause the steel to brittle and break.
Sulfur is also present in a very tiny amount of 0.03% and just like Phosphorous, is considered an impurity. However; it also helps to improve the steel’s machinability.
P20 mold steel is typically acquired from the supplier in a pre-hardened condition, thus, hardening heat treatment is not necessary.
In rare cases, if the tool steel needs to be re-hardened, it must first be annealed before hardening.
Annealing refines the grain, increases ductility, and eliminates internal stresses. The mold steel is heated to approximately 222ºC /400ºF per hour and up to 788ºC / 1450ºF and equalized. It should be held for 1 hour per inch / 25.4 mm of maximum thickness for approximately 2 hours. The steel is now cooled slowly to the ambient temperature in the furnace or the air.
Stress relieving is carried out to eliminate machining stresses to prevent deformation. In the case of P20 tool steel, stress relieving should be carried out by heating the steel to approximately 650oºC /11732ºF for 1-2 hours. The steel is further air-cooled.
Hardening is carried out to balance the toughness of the steel. In the case of AISI P20 tool steel, it’s uniformly heated to approximately 820°C / 1508°F. It’s further quenched in oil, air, or warm water. Generally, the hardness level after quenching is 51 HRC and other hardness levels can be achieved via additional heat treatments.
After quenching, the steel is tempered immediately. During this process, the steel is held at a specific temperature for 1 hour per inch / 25.4mm of thickness for a minimum of 2 hours after which it is air-cooled. The tempering temperatures versus the hardness are mentioned below:
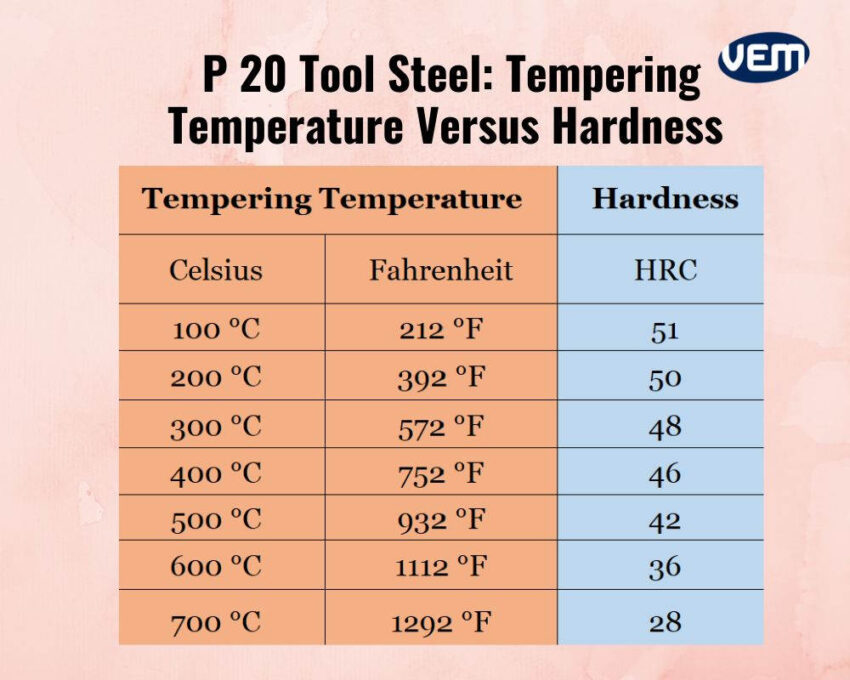
P20 tool steel is easily machinable. In its pre hardened condition, it’s machinable at a rate of 65%.
Forging is a process that is applied to shape the steel through localized compressive forces such as hammering or pressing. Forging helps manufacturers to produce high-quality steel products with exceptional tolerances.
P20 mold steel can be forged within a temperature range of 900°C to 1093°C /
1652°F to 1999°F.
P20 mold steel can be welded through all conventional processes. Its excellent weldability along with other characteristics makes it popular among plastic mold makers.
P20 Tool Steel is a low alloy steel that has unique properties. It is crucial to understand the specific characteristics of the various types of steels to create a well-designed mold.
VEM-Tooling has a vast experience of over 20 years in building mold design. Our team of design experts and engineers can guide you with the correct steel for your manufacturing solution.