

Imparting color plays a crucial role in injection molding processes to manufacture products according to the specific vision of the part. There are various processes through which color can be added to the injection molding process and one of the most popular processes is color masterbatch.
A color masterbatch is typically a collection of highly pigmented plastic pellets that cannot undergo injection molding by themselves. These pellets are thus mixed with uncolored plastic pellets so that the color combines with the plastic, thereby creating an overall color that is tailored and unique to the project requirement. In this article, we discuss various parameters and specifications of color masterbatch in detail.
The color masterbatch is also referred to as color type or color concentrate. The primary purpose of color masterbatch is to color polymers with specific hues and tones. You should note that a color masterbatch can be engineered to manufacture any type of hue in the color spectrum.
A color masterbatch is a type of pigment blend that is injected and mixed into raw polymers and is employed for coloring thermoplastics during the manufacturing process. A color masterbatch is highly concentrated and its composition can consist of one or more colorants.
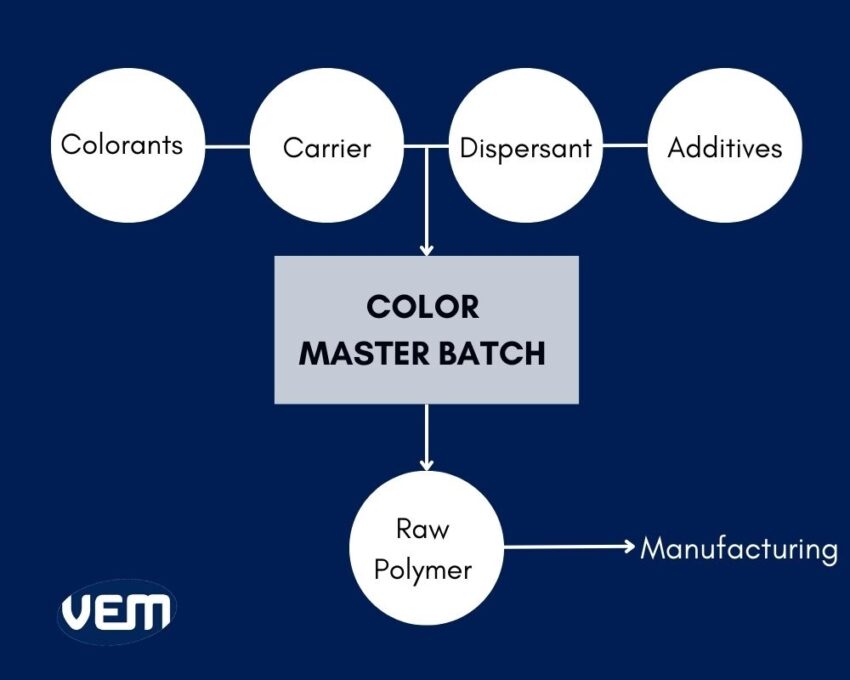
The color masterbatch is obtained by distributing pigments and additives into a polymer carrier by heat treatment and a high-shear mixing extruder. This mixture is cooled off, cut, and formed into granules via a pelletiser. The pigments are uniformly loaded in an ultra-constant amount and this is also referred to as the pigment concentration. The range of additives is typically between 40-65 % but in exceptional cases, this range can be altered to be between 15-80 %.
Color masterbatch is further categorized into the following types:
A color masterbatch consists of four elements i.e. colorants, carriers, dispersants, and additives. This composition is referred to in the industry as its recipe. Let’s understand these components further:

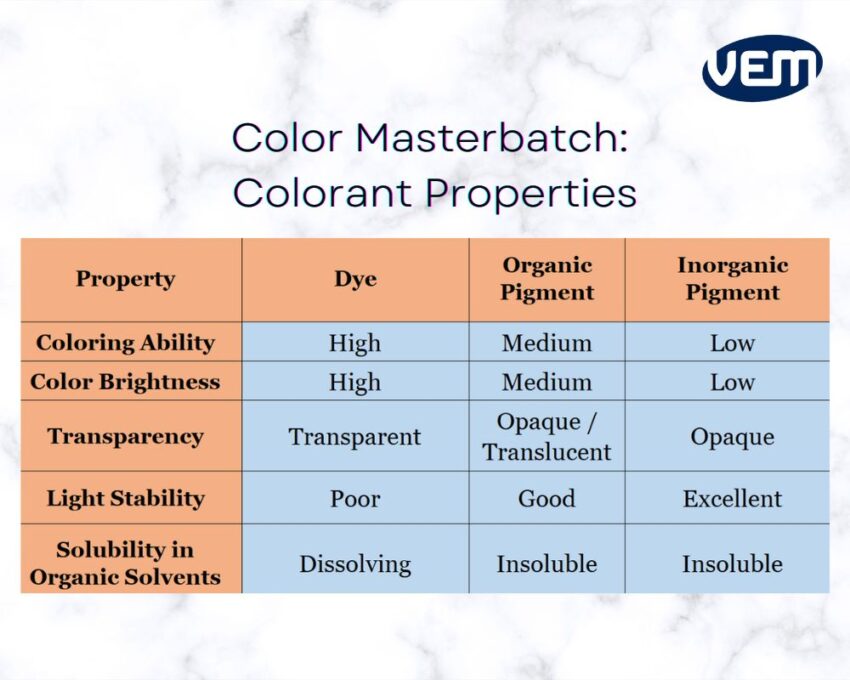
Colorants are further classified into several categories such as organic dyes, organic pigments, and inorganic pigments.
You should note that dyes can be used for transparent coloration as they are soluble in plastics whereas pigments remain intact in their original particle form inside the plastic which is why they need to be dispersed within the plastic.
Some of the most commonly used organic pigments are phthalocyanine red, phthalocyanine blue, phthalocyanine green, light fast red, macromolecular red, macromolecular yellow, permanent violet, azo red, etc., and inorganic pigments are cadmium yellow, titanium dioxide, carbon black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, etc.
The following table enlists some of the properties of the colorants:
A carrier is one of the most essential components of color masterbatches and it serves as the base material to hold and disperse the colorants uniformly throughout the plastic.
A carrier in a color masterbatch acts as a dispersion medium that ensures that the colorants are uniformly blended with the polymer. In addition, carriers provide compatibility with the polymer which enables easy processing.
There are several types of carriers and they are chosen as per application and compatibility with the target polymer. Let’s understand the various types of carriers:
Dispersants in color masterbatches avoid the flocculation of pigments and dyes. They promote uniform dispersion of the colorant. To ensure that there is no agglomerate, the following should be noted:
Some of the most commonly employed dispersants in color masterbatches are polyethylene low-molecular wax and stearate.
The additives in a color masterbatch can permanently modify the properties of the plastic. It is included only when it is required for the project and requested by the customer. Some of the properties that additives can impart are flame-retardant, anti-bacterial, anti-static, anti-oxidation, etc.
Silk-like Polymer Alloy Masterbatches impart silk-like luster through polymer alloy technology and exhibit high color saturation and brilliance.
Frosted masterbatches impart a frosted glass-like appearance without processing the mold surface.
Anti-yellowing color masterbatches have a highly dispersed titanium oxide and are excellent in suppressing yellowing caused by titanium.
Low-shrinkage pigments exhibit excellent color stability and high dispersion. This type of color masterbatches avoids plastic warping or distortion in molded parts.
Black and white color masterbatches are common color masterbatches that have a high functional value.
A white masterbatch is often used to create plastic parts with coating and laminations whereas a black masterbatch is employed to manufacture black-colored products. You should note that black color masterbatch can also be designed for a wide range of color depth and crystallization.
The primary goal of determining the color masterbatch ratio or proportion is to achieve a uniform coloring effect with no streaks, spots, or defects. Let’s understand the various ratios:
The 1:100 ratio is the most cost-effective ratio of color masterbatches however; it is not recommended to use this particular ratio as uneven pigment dispersion is likely to occur.
1:50 color masterbatch ratios are employed for general coloring requirements. They are mostly used for Polyethylene and Polypropylene color masterbatches.
The 1:20 color masterbatch is employed for advanced plastic parts and can be used for a variety of processes such as injection molding, blow molding, and other processes, etc.
This particular ratio is typically employed for coloring high-grade cosmetic containers. It is also mostly used in small injection molding machines.
If the color hasn’t developed as per the ratio i.e. if it’s too light or dark, then the following needs to be considered:
Color Master-batch is employed in various industries such as the electronics, automotive, agriculture, construction, packaging, and textile industries. Let’s take a look at some instances:

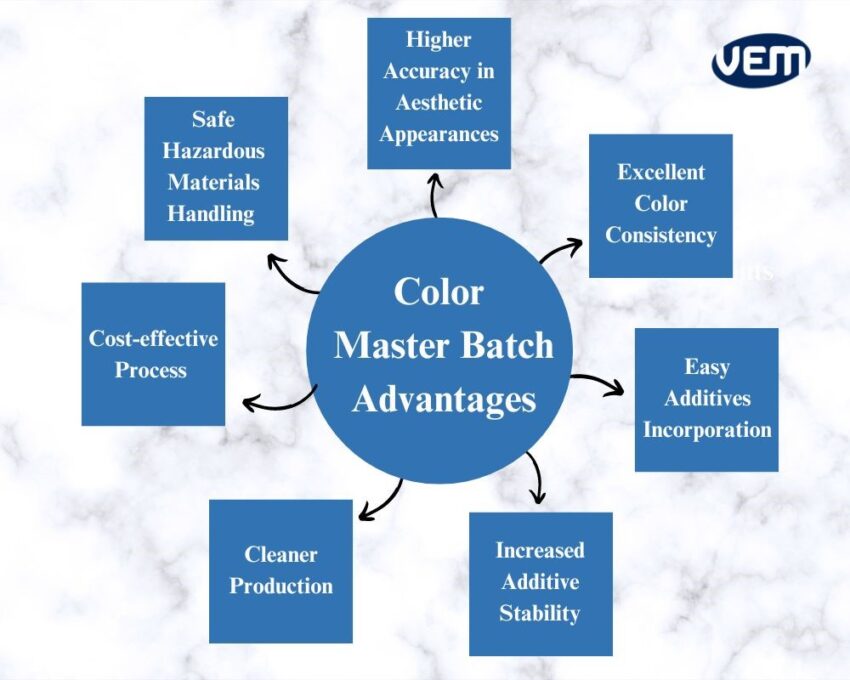
Since the additive ingredients are pre-determined, the chances of variance during the manufacturing process are minimal thus, color masterbatches enable higher accuracy in aesthetic appearances. They help in delivering accurate transparency and opacity consistently in the products.
You should note that since the binding agents in masterbatch are matched with target polymers, the melting processes are improved which helps color masterbatch to deliver excellent color consistency, especially during large production runs.
Color masterbatch reduces the complexity of mixing pellet-to-pellet and it eliminates the requirement of a special dosing device in case of minute quantities.
Color masterbatch increases the stability and shelf-life of additives. It helps to protect additives from various environmental factors such as exposure to humidity, temperature, and UV during storage.
Many additives can be hazardous in their raw formulations. In the case of masterbatches, the additives are encapsulated in a polymer resin or a liquid form thereby, reducing its unsafe nature. This not only helps to reduce its hazardous effects but also helps to reduce the requirements for personal protective equipment and technical controls.
Masterbatch additives are not only safer to handle but they also enable cleaner production. During processing, pigments, unlike color masterbatch, can become airborne, which results in contamination. In the case of color masterbatch, no powdered additives or color pigments attach to surfaces which reduces cross-contamination, and thereby, cleaner production areas.
Purchasing colored raw polymers is relatively more expensive than uncolored polymers. In addition, they can be stocked for use with various types of color masterbatch.
Color masterbatch is relatively simple however; some precautions must be noted. These are enlisted below:
Color Master Batching requires skilled expertise to produce high-quality parts. It is crucial to understand the various aspects of the technique so that the specific requirements of your project are met.
While we are more focused on injection molding and tooling, we also cater to various services such as prototyping, retail assembly, and more. You can connect with us for any query, and our team of experts will connect with you.