

The manufacturing industry is constantly evolving and upgrading itself to the latest technologies! Today, many manufacturers are using Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies to assist workers on the plant floor. Digital transformations are among the industry 4.0 technologies that are enabling manufacturers to streamline production processes thereby, helping them to compete with the global market.
Today, various digital technologies are gaining popularity as they help manufacturers to increase efficiency, lower costs and push for faster deliveries. These technologies are integrated with manufacturing processes and they help to improve operations, processes, and customer value. New technology also encourages manufacturers to innovate further!
Digital manufacturing integrates computer technologies to improve manufacturing operations. Businesses that implement digital systems can easily adapt to customer requirements and are more agile. They are able to enhance productivity and accuracy! According to a study conducted by Deloitte and MAPI in 2019, it was observed that small factory initiatives, a digital

manufacturing type, has led to an average of 10% increase in production output and an average of 11% increase in factory capacity. You can read more about this study by Deloitte in detail here.
Manufacturing facilities are continually increasing automated tools on the plant floor to digitize the systems. It thus helps engineers to monitor, analyze, and model all machines in order to optimize processes. The goal of digital manufacturing is to increase efficiency and flexibility while ensuring leanness in resources.
This article is an in-depth and definitive guide to understanding digital manufacturing, its benefits, and use cases.
Digital manufacturing primarily involves using an integrated, computer-based system to develop manufacturing processes. Its approach is to combine manufacturing operations with computer systems to improve machines, processes, and productivity. These computer-based systems refine and optimize manufacturing processes through simulation, 3D visualization, analytics, and collaboration tools.
Digital manufacturing evolved from various manufacturing strategies and processes such as lean manufacturing, design for manufacturability, and computer-integrated manufacturing processes. These processes highlighted collaborative designing requirements. You should note that it is not possible to achieve long-term solutions in product lifecycle management (PLM) with simply one strategy and thus, a comprehensive approach is needed. Digital manufacturing integrates PLM and operational processes thus, enabling information exchange.
These technologies can also simulate the entire manufacturing cycle and the data that is obtained from here, can be used for further optimization. It also helps to speed up production and reduce operating costs. These technologies link systems and processes across the production cycle to create an integrated approach that is all the way from design to production and finally, product servicing. Today, digital technologies are becoming increasingly popular across the globe as real-time analytics effectively decreases inventory and bottlenecks.
Digital manufacturing tools are often cloud-based. They are designed to connect and simplify manufacturing processes. This is throughout the production cycle. These tools create a ‘digital thread’ which integrates itself into the manufacturing operations. The data collected is now used to streamline operations and enhance design, production, servicing, and more.
Digital tools enable manufacturers in managing the entire manufacturing process through a centralized platform. They open up the possibilities of collecting and analyzing data across the production cycle. The data that is collected through digital tools allow manufacturers to understand if certain areas of production need maintenance or they need to be optimized.
These tools also allow customer data to be sent to product managers. This enables demand anticipation which further, allows delivering products via manufacturing. Due to the latest rise of AI, we can anticipate to see a whole selection of new tools. Currently, AI tools are mostly used in more digital industries, such as writing helpers.
Smart manufacturing, which is another term for digital manufacturing, is an extremely organized operational segment that comprises various departments and roles. These range from business development and sales to supply chain, engineering, cloud architects, and cybersecurity. Let’s take a look at some of the personnel roles in digital manufacturing:
Digital manufacturing is of 3 types. Each type corresponds to a particular aspect of the manufacturing process. These range from product design and innovation to customer satisfaction and resource management. It is thus applied to three main areas of the manufacturing cycle i.e. product life cycle, value chain management, and smart factory. Let’s understand these types further in detail:
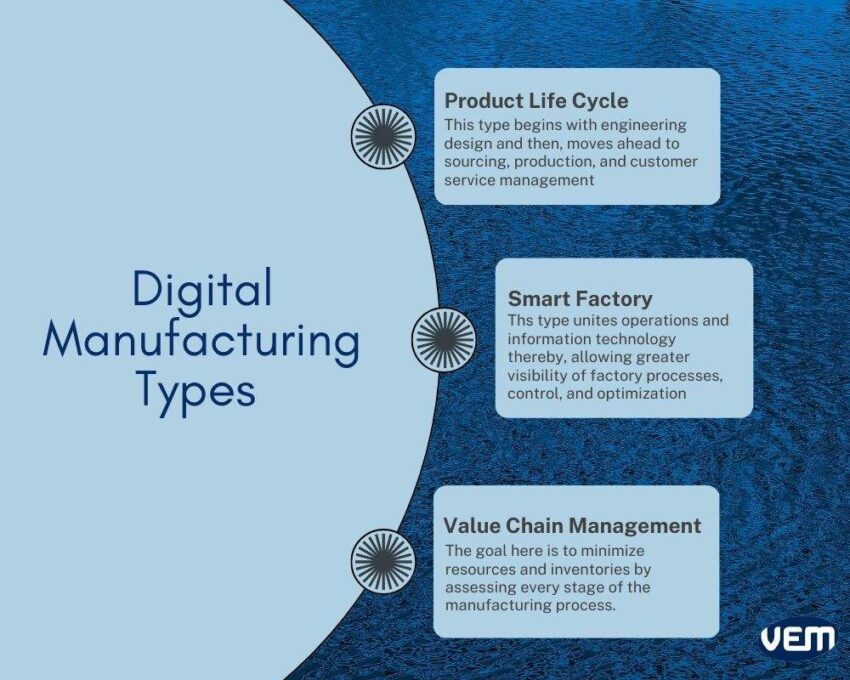
This type of digital manufacturing begins with engineering design and then moves ahead to sourcing, production, and customer service management. Each step in the product life cycle management uses digital data and analytics. This data is used to incorporate revisions to the design specifications, anticipate the requirements of raw materials, and provide better customer service.
Smart factory digital manufacturing unites operations and information technology thereby, allowing greater visibility of factory processes, control, and optimization.
Digital manufacturing of the smart factory type uses smart machines, sensors, and tooling. The real-time data that is gathered here, are insights that are used to increase process efficiency. These insights are further used to change processes to boost productivity and reduce costs. The main aim here is to help workers receive real-time data on the functions and processes that are being performed by them. This feedback connects the operations teams that monitor the machines with the IT teams that deal with the back-end systems.
The value chain management type focuses on reducing additional resources without compromising product quality and customer satisfaction. The goal here is to minimize resources and inventories by assessing every stage of the manufacturing process.
Today, digital manufacturing is applied across a wide range of industries to create various products. Let’s understand these use cases further:
Digital manufacturing technologies are specifically applied to obtain data and analytics as they can help to obtain actionable insights for demand forecasting. It is thus possible to understand if certain equipment modes are failing. Manufacturers can also use predictive analytics through the data and analytics tools to continuously make adjustments to maintenance schedules.
For instance: An automotive manufacturer can incorporate supply-network management tools to evaluate raw materials flow and manufactured parts to ensure operational efficiency.
Digital technologies can be incorporated to plan for predictive maintenance of equipment by manufacturers. These technologies allow engineers to analyze and assess data through sensors. The data that is obtained through these sensors can help manufacturers to predict if the equipment is likely to fail. It helps them to not only take preventative action but also to build a predictive maintenance plan to avoid any type of downtime.
Cloud computing tools enable suppliers to collaborate efficiently! It increases transparency thereby, reducing risk. It is possible to share 3-D simulation models of a complete production line and gather details for RFQ i.e. request for quote process. These details can include pricing, quality, raw material, and delivery from various suppliers.
For instance: The aerospace industry popularly uses cloud computing tools to integrate its complex supply network such as manufacturing a jet engine, which may require several hundreds of individual parts.
Digital manufacturing evolves and streamlines manufacturing processes. It helps manufacturing companies improve productivity through efficient planning. There are various benefits of creating an automated data exchange across processes. Let’s take a look at some of its benefits:

As seen above, digital manufacturing does offer various advantages but it is not limited to just optimizing processes and reducing costs and time. It also plays an efficient and evolving role in manufacturing environments and design phases. Let’s understand this further:
Digital manufacturing allows an entire manufacturing process to be created and delivered virtually. This helps the designers and manufacturers to test processes before they invest extensive resources into physical implementations. It basically allows the testing of simulated processes! Furthermore, it’s extensively agile which allows design changes to be made in real-time thus, if any changes are required, it can be done so without stopping the production line.
This technology can develop models to ensure that the processes can operate under optimal layout and material flow. It also enables the manufacturers to develop a preventative maintenance program. This program utilizes sensors and data collection to reduce costs. Software is integrated with sensors that can report on product quality in real time. This helps businesses to be proactive in tuning processes in case of a defect.
Digital manufacturing also offers various design advantages! They incorporate 3D modeling software to design tools, production flows, machinery, and factory floor layouts. It is also possible to monitor systems in order to assess deviations from the set protocols. This technology can also be used to make fast, almost instantaneous changes to product designs if something is not suitable. This can be achieved through cloud-based designs.

Digital Manufacturing poses various advantages but implementing the same has some challenges. Let’s understand what are some of the most commonly seen digital manufacturing challenges:
Digital transformation does bring a positive change in the manufacturing process but when a new system or solution is being implemented, it often adds to the costs. The budget may be limited and may not always support the implementation of digital technologies.
Digital technologies are expensive and they transform processes hence, you must ensure that the digital technologies that are being implemented should include strategies and plans for the future. This requires detailed strategizing and can be sometimes challenging if not approached in a systematic manner.
Implementing digital transformations especially leads to extensive IT challenges. Manufacturers and engineers must plan for fiber optics, servers, and long cable runs in order to implement digital transformations.
When implementing new technologies, there are often behavioral constraints from the staff. It’s because they are used to certain processes and they have been doing the same, for decades.
Implementation of new technologies is often met with distrust in the beginning thus, it is important to not only give process training to the staff but also explain to them the relevance of utilizing digital technologies.
Data security is definitely a cause of concern when we talk about the implementation of digital technologies. Most of the systems are cloud-based and they operate over the Internet. IoT security does pose a risk of hacking, but it can definitely be mitigated to the lower end by implementing security protocols.
ERP, abbreviated for enterprise resource planning is a software that helps businesses achieve efficiency! ERP software can transform your manufacturing business with its modules and robust features.
It is a software tool that centralizes all the departments and their functions in one place. ERP creates a vase through which you can make informed business decisions, analyze data and act upon emerging opportunities. An ERP system not only centralizes operational processes but also bridges customer requirements.
This software enables organizations to digitally transform processes and incorporate other 4.0 technologies such as IoT (The Internet of Things), machine learning, and robotics. These technologies help manufacturers to work more efficiently! ERP does not cater to only the production area but also helps with quality control and supply chain management.
Traceability is the ability of a tool to track a product through its value chain. Traceability tracks the product all the way from raw material sourcing to final product disposal. It is one of the most important factors in the manufacturing industry and ERP software does just that! It enhances traceability and helps manufacturing companies locate anomalies. It also helps to identify their causes thereby giving the engineers the ability to eradicate the errors in the future.
In order to facilitate traceability, manufacturing companies need ERP tools that can ensure relevant data collection and distribution of the same. Thus, ERP ensures safety and enhances quality in the manufacturing industries.
There are various ERP systems available but there are a few that are suited for the manufacturing industry. The following ERP systems are designed to help manufacturers across various processes. Let’s take a look at some of the top ERP systems that are suited for the manufacturing industry:
Today, ERP captures data for organization and analysis and automates workflows. It is expected that in the future, ERP will garner the capability of using artificial intelligence and machine learning. It will be able to use these 5.0 technologies to provide guidance, accurate precision and extend decision-making analysis. It is expected that ERP can help business leaders understand the unknowns and prepare for them in the future.
It is inevitable that the need for modern digital technology will continue to increase!
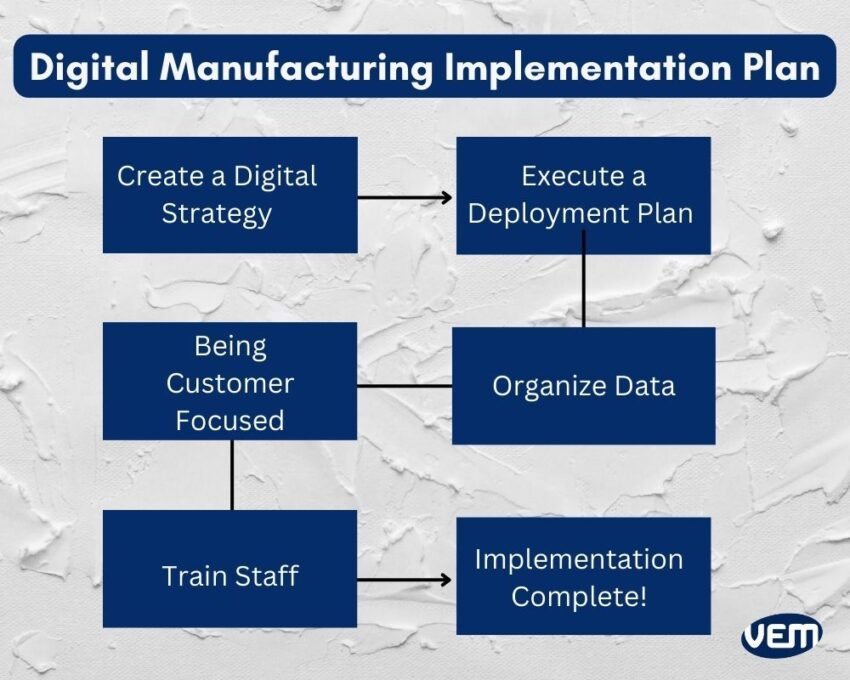
One has to keep up with the new age and customer requirements so if you plan to introduce digital transformations in your manufacturing process, here are some steps that you should consider following:
Creating a digital strategy is crucial as it helps you to build a foundation! You should evaluate to determine how to further hone your operational processes. After you have discovered the areas that need to be controlled and harnessed, you can move ahead to creating a digital strategy. Your executive team will need to be involved in supporting digital transformation efforts.
The entire manufacturing team i.e. the engineers, designers, and executives need to understand what is the best way to implement the software and digital transformations. You should elaborate upon timelines and each individual’s roles. You should also make a note of the best practices that should be followed to plan implementation!
If needed, you should restructure some processes to ensure that they are compatible with the implemented system.
Organizing data is one of the most crucial aspects of digital transformation as this helps you in adding correct and accurate data to the system. If the input data is not correct, then the output data won’t be correct either. Once the data is entered, the system keeps all the data in a centralized database so that everyone receives the same real-time information.
When you plan for implementation, you must keep in mind to optimize the technologies to provide an excellent experience for your customers! The goal of implementing digital manufacturing technologies should be not only to optimize processes but to make your customer experience efficient and exceptional services. This will enhance customer satisfaction levels and increase growth!
In order to achieve great results, you must train your staff to use the technologies! Your staff must be fully trained and as you prepare them to adopt new digital technologies, you should also explain to them the benefits it offers to the company, customers, and themselves. This will give them an in-depth understanding of the transition to digital technologies.
Digital manufacturing has unlocked an array of opportunities for product designers, developers, and manufacturers. These technologies streamline workflows and reduce errors! It has introduced new potential in how we design, evaluate, and manufacture parts.
A modern manufacturing system that includes Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies, lets manufacturers improve processes, enhance the customer experience, gain insight, and reduce costs.
At Vem-Tooling, we have increased our implementation of digital manufacturing technologies over many years. Our team has vast experience in utilizing the newest technologies to increase efficiency and quality. The quality of our molds and traceability during the process, represent VEMs achievements in digital manufacturing. Experience it yourself, and contact us for your next plastic project.