

Regulatory authorities enforce strict regulations on industries such as medical devices, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, automotive, and aerospace. In such cases, even minor inconsistencies can have a significant impact on the product quality, which is why process and equipment validation are crucial. It ensures that the manufacturing process consistently produces products as per the predefined quality standards.
In a manufacturing industry, the validation process has three stages:
It is crucial to carry out and document all three validation stages, as they assess various aspects of the equipment, processes, and systems. Together, these stages ensure that the manufacturing process is robust and reliable. In this article, we discuss each of these stages in detail and enlist a case study of its application in the injection molding industry.
IQ, OQ, and PQ are protocols that manufacturers incorporate to validate manufacturing processes.
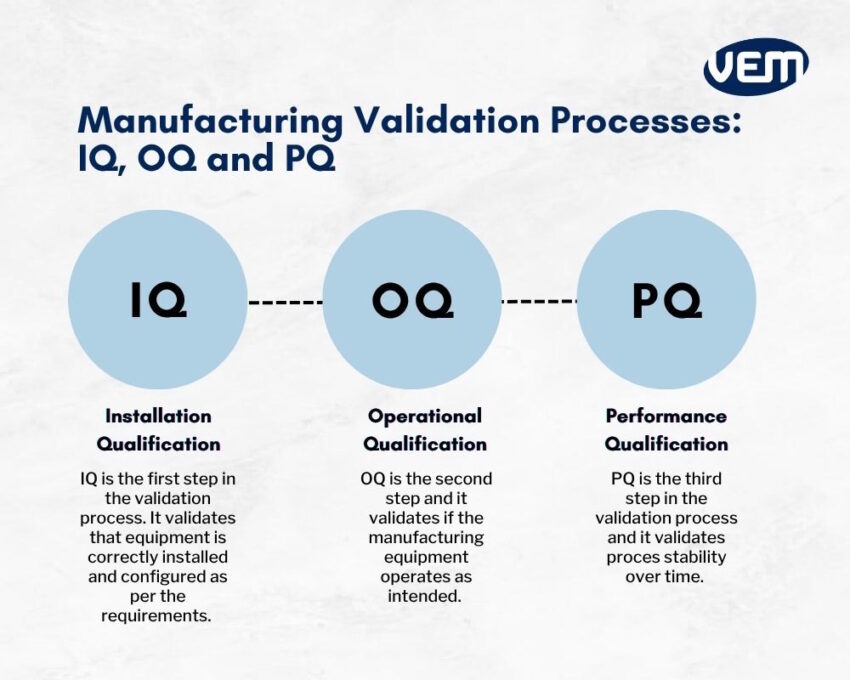
The term IQ stands for installation qualification, OQ for operational qualification, and PQ for performance qualification.
The IQ, OQ, and PQ protocol establishes documented evidence. This further ensures that the production equipment is installed correctly, safely, and operates as per the requirements. In addition, these processes ensure that the manufacturing processes consistently deliver products that meet required standards.
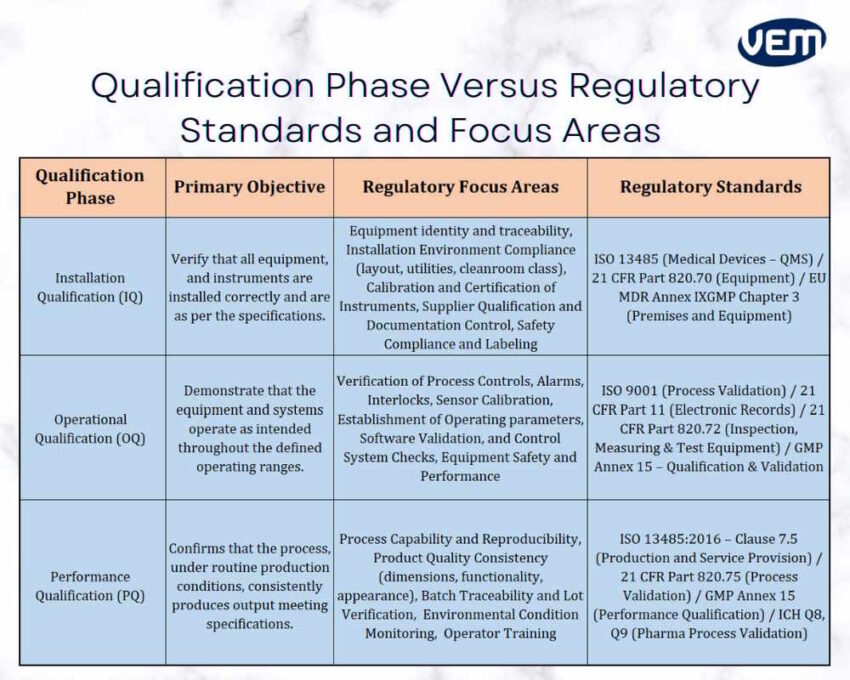
Manufacturers conduct IQ, OQ, and PQ validation according to regulatory focus areas and standards to ensure compliance.
IQ, OQ, and PQ protocols follow a structured approach, and their framework enables manufacturers to maintain compliance with international quality standards and regulatory bodies across various industries. The infographic below indicates qualification phases and their respective regulatory areas:
In the manufacturing industry, equipment and process validation follow a sequential order. Each stage is important and builds upon the last stage. Let’s understand the various stages involved in the validation process:
The first step is to document all the requirements in a User Requirement Specification document. In this document, the manufacturer defines the testing criteria.
In this stage, manufacturers develop detailed IQ, OQ, and PQ protocols. These protocols specify all the test procedures and acceptance criteria.
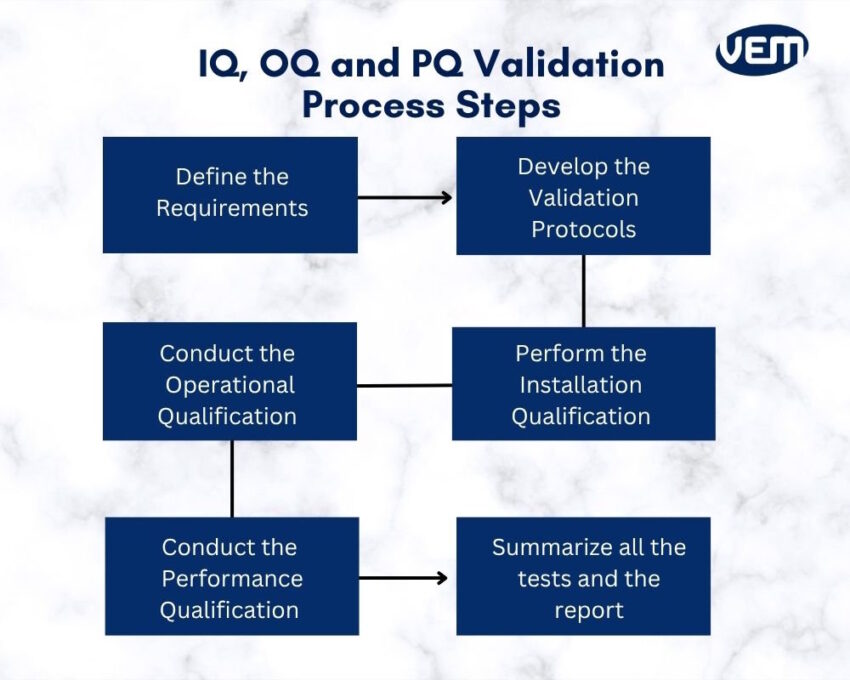
The manufacturer performs the IQ protocol. Through this protocol, they verify that the installation meets the design specifications.
The next stage is to perform the operational qualification. In this phase, the manufacturer performs the OQ to test and document whether the equipment and systems operate as per the protocol.
Once the manufacturer completes IQ and OQ correctly, they proceed to PQ. This phase confirms that the manufacturing process produces the desired quality product consistently.
In the final stage, manufacturers summarize all the results to create the report. Once the manufacturer prepares and approves the final validation report, production can commence.
IQ in manufacturing is the first step in the validation process. It ensures that manufacturers install every equipment, service, and instrument correctly. It also ensures that all installations follow the manufacturer’s requirements.
Manufacturers consider an installation qualification successful when the installation process meets all requirements and manufacturer guidelines. You should note that the IQ phase lays a foundation for the subsequent qualification phases.
The IQ documentation provides a comprehensive outline of the scope and criteria for conducting installation qualification validation. It should include the following details:
IQ protocol includes a detailed checklist, which guides manufacturers to conduct all the tests.

Installation qualification validation is a detailed process that includes various multiple parameters. In this phase, it’s crucial to compile all the necessary documents, drawings, and manuals. It is also necessary to establish equipment maintenance, calibration schedules, and procedures.
The installation qualification report documents the entire protocol execution and should clearly state whether the equipment and services meet the predefined criteria. It summarizes the findings, observations, and results to ensure that the installation is correct.
Operational qualification forms the second phase, following IQ validation. It identifies and verifies whether the equipment can operate in accordance with the manufacturer’s requirements.
During operational qualification, manufacturers test various functional aspects of the equipment, such as temperature and pressure settings. These tests verify and confirm that each component of the manufacturing equipment operates as intended. This ensures a reproducible manufacturing process.
The OQ documentation is similar to IQ and follows an extremely structured process. The documentation defines normal operating conditions and confirms that the equipment operates within specified process parameters.
Manufacturers test the equipment extensively to determine process control limits, potential failure modes, and worst-case scenarios. During operational qualification, manufacturers test all process parameters outlined in the plan and document their performance accurately and in detail.
OQ documentation includes a detailed review of hardware and software startup, operation, maintenance, cleaning, and safety procedures. It should also include protocols, checklists, and standard operating procedures for equipment use.
The OQ protocol outlines the objective, scope, methodology, and acceptance criteria for the OQ validation process.
Operational qualification checklists provide detailed instructions and specify the exact steps for executing each test. It also includes expected outcomes based on the acceptance criteria.
Standard operating procedures play a crucial role in ensuring that the equipment is operated correctly. The OQ protocol must reference all relevant SOPs to ensure proper equipment testing.
The documentation includes procedures not only for operating the equipment but also for handling deviations, maintenance, and calibration.
Just like installation qualification validation, the operational qualification report is also extremely detailed. Some of the key checkpoints for performing OQ are listed in the infographic below:

The operational qualification report includes a summary of the findings. It should also include details of whether the equipment has successfully cleared the OQ validation tests.
Performance qualification is the last step of the validation process. In this phase, the manufacturing team verifies process stability over time. The equipment is run several times under normal operating conditions to evaluate its functionality. PQ protocol demonstrates whether the manufacturing process can produce parts that meet requirements for an extended period of time.
IQ and OQ, focus mainly on equipment and operational limits. PQ, however, focuses on the overall process to ensure its reliability in manufacturing consistent quality products. The performance qualification phase tests all the instruments together as per the test plan.
Performance qualification documentation focuses on consistency and reproducibility, data traceability, and maintenance manuals and documentation.
The main aim of PQ is to ensure consistency and reproducibility. In this phase, the performance is not only tested over an extended period of time and under typical operating circumstances, but also worst case scenarios.
This validation process phase supports data traceability. The team incorporates data backup and audit trails to facilitate traceability.
The manufacturing team includes Standard Operating Procedures and maintenance manuals for thorough documentation. These are available to all users of the equipment.
The performance quality report includes the entire data summary. It’s a detailed and comprehensive report, and the infographic below lists key checkpoints for performing PQ:

This is a case study for manufacturing highly accurate and precise plastic housings and components for a personal-use digital blood pressure (BP) monitoring device. The parts required tight dimensional tolerances, optical-grade clarity for the display window, and biocompatible materials that are compliant with ISO 10993.
To ensure quality and regulatory compliance, the team carried out a complete IQ, OQ, and PQ validation process.
During the installation qualification phase, the injection molding company verifies that the molding equipment and its supporting units are installed as per specifications.
The team confirms that the molding machine model, tonnage, and serial number align with the documented plan. The engineers check the foundation level, vibration isolation pads, and anchoring to ensure stability. They also test utility systems such as power supply, cooling water, and compressed air for consistency and compliance. This ensures that the production environment is controlled and capable of supporting medical-grade molding operations.
The molding tools for BP device components, such as the outer housing and control buttons, were installed and inspected for correct alignment, proper venting, and surface finish quality. The team also tested safety systems such as guards and interlocks to verify functional integrity.
Lastly, the manufacturing team compiles and reviews equipment manuals, calibration certificates, maintenance logs, and validation documents. It ensures that the machine and tooling setup are stable, safe to operate, and meet regulatory expectations under ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
In the operational qualification phase, the injection molding company verifies that the machine, mold, and supporting systems for the BP monitoring device operate reliably and within their defined performance limits.
The molding team tests for critical process parameters such as injection pressure, melt temperature, cooling time, etc. to confirm that they operate well. The team also tests the accuracy of temperature controllers, and hydraulic systems, against calibrated standards, to ensure stability in the molding cycle. These tests ensure that every function of the equipment performs as required.
Defining and verifying the limits in the operational qualification protocol enables the injection molding company to minimize defects, reduce risks, and ensure compliance with medical manufacturing standards such as ISO 13485 and GMP Annex 15.
In the performance qualification validation phase, the manufacturing team conducts multiple production runs with the polymer using the parameters established in the OQ validation phase. In addition, the manufacturing team continually monitors environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity.
environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity are continually monitored to ensure that the BP device components are stable, functional, and compatible with sensitive electronic assemblies during final device integration.
The engineers evaluate and inspect BP device components using calibrated instruments. They also perform visual inspections to detect flow lines, warpage, or other defects. The quality team evaluated each batch for dimensional accuracy, part weight, color consistency, and surface finish.
The engineers applied statistical process control to evaluate consistency. Cp and Cpk values were calculated for critical dimensions such as housing snap tolerances. Any deviations were documented, and analyzed. They were further resolved through corrective actions.
An approved PQ validation phase ensured that the injection molding process is repeatable, and ready for continuous production. It also demonstrates regulatory compliance with ISO 13485 Clause 7.5 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820.75.
IQ, OQ, and PQ validation phases optimize processes and enable regulatory compliance. The systematic approach is an essential component for a robust quality management system.
VEM Tooling has an extensive experience of over 20 years in tool building and manufacturing high-quality parts. Our experienced engineers can guide you throughout the IO, OQ, and PQ validation phases and other manufacturing solutions, such as injection molding and tool building.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.