

Thailand is a well-established manufacturing hub due to its strategic location, developed infrastructure and factories, skilled workforce, and supportive government policies.
Thailand is a dynamic manufacturing destination in Southeast Asia. Over the decades, it has demonstrated decades of steady growth and a robust industrial base, which is why it is a preferred destination for global manufacturers. In this article, we discuss various details of manufacturing in Thailand, such as its free trade agreements, its industrial regions, and manufacturing clusters in detail.

Thailand’s free trade agreements are key driving factors for its economic integration globally. Thailand actively integrates Free Trade Agreements for its trade and investment strategy. These agreements either eliminate or reduce tariffs.
In the past two decades, Thailand has signed various bilateral and multilateral free trade agreements, thereby enhancing its global trade profile. Through these agreements, Thailand has integrated further into global supply chains and attracted foreign direct investment.
Thailand is one of the founding members of ASEAN, abbreviated as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, and thus, benefits from reduced tariffs among member states and facilitates the flow of goods and services within Southeast Asia easily. In addition, CEPT, abbreviated for the Common Effective Preferential Tariff scheme, has significantly reduced tariffs on intra-ASEAN trade.
You can read more about Sourcing and Manufacturing in Southeast Asia here.
Thailand has specific FTAs with individual countries. These agreements provide preferential access to some of the world’s largest economies such as Australia, New Zealand, Chile, Laos, Peru, China, Japan, South Korea, and India.
RCEP, abbreviated for Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, was signed in 2020 and has been effective since 2022. RCEP is the world’s largest trade pact, which involves 15 countries, including ASEAN members. The RCEP aims to deepen regional supply chains and reduce trade barriers across the Asia-Pacific region.
The negotiations for the EU-Thailand FTA resumed in 2023 with the aim of a comprehensive and balanced agreement. The objective here is to enhance trade and investment, thereby focusing on market access, sustainable development, and digital trade.
The negotiations for EFTA are ongoing. The members of EFTA are Liechtenstein, Norway, Iceland, and Switzerland.
Thailand’s Free Trade Agreements have had several economic impacts. Let’s understand their contribution in this section:
Free trade agreements have diversified Thailand’s export destinations. They have also reduced dependency on traditional markets.
Free trade agreements in Thailand have helped to attract foreign investors, which has resulted in the growth of FDI, abbreviated as Foreign Direct Investment.
Free trade agreements with developed economies have aided in technology transfer by bringing in advanced technology and improved industrial capacity.
Manufacturing clusters are advantageous to investors as they facilitate easy connections among manufacturers, suppliers, supporting industries, research and academic institutions, and public and private organizations within the cluster areas.
The government of Thailand implemented this policy in 2015 and is continually improving these regions. These are referred to as the Cluster-based Special Economic Development Zones Policy. Let’s understand some of the major manufacturing clusters in Thailand:
Thailand is a top automotive manufacturer in Southeast Asia and accounts for 13.12% of Thailand’s exports. Since it’s a major manufacturing hub for automotive parts and is one of the largest global exporters, Thailand is also referred to as “The Detroit of Asia”.
Thailand’s automotive manufacturing clusters are strategically concentrated in the Eastern Economic Corridor, which spans the provinces of Chonburi, Rayong, and Chachoengsao. These regions are geographically connected through excellent infrastructure such as deep-sea ports, i.e., Laem Chabang, direct highway links to Bangkok, and Suvarnabhumi International Airport. The automotive manufacturing region also includes specialized industrial zones such as the Eastern Seaboard Industrial Estate and Amata City, which includes a dense network of Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 suppliers and original equipment manufacturers.
Thailand’s automotive production facilities are among the most advanced in the ASEAN region. Many plants in the automotive sector operate under global standards of ISO/TS 16949 and ISO 14001, and are equipped with robotics, automated assembly lines, and smart manufacturing systems.
In recent years, Thailand has emerged as a growing hub for electric vehicle and battery production. These developments are reinforced by a localized supply chain that includes lithium-ion battery assembly, motor systems, and EV charging infrastructure. The government has introduced “EV 3.0” and “EV 3.5” policies to facilitate tax exemptions and reduce import duty for EV and battery manufacturers.
Thailand is well-known for its manufacturing of electronics and electrical appliances, including hard disk drives, cables, integrated circuits, computer components, diodes, semiconductors, etc. It’s a major exporter of computers, electronic integrated circuits, telephone sets, air conditioners, internal combustion engines, refrigerators, and freezers.
The electronics and electrical appliance cluster currently spans 7 provinces that are neighbouring Bangkok. Bangkok has approximately 800 factories manufacturing electrical appliances.
Thailand is a significant manufacturer and exporter for the medical device industry. It is also regarded as an innovation hub in the ASEAN region. There are over 700 medical device manufacturers that produce a wide spectrum of devices, that range from disposable items such as surgical gloves, syringes, and PPE, to more advanced equipment such as diagnostic imaging systems, dental instruments, and patient monitoring devices. Thailand’s medical device manufacturers deliver high-quality parts that are compliant with international standards such as ISO 13485 and CE marking.
The medical device manufacturing cluster of Thailand is mainly located in the EEC, where manufacturers benefit from state-of-the-art infrastructure, skilled labor, and partnerships with leading research institutions and hospitals. The emerging trend of Medical Supplies made in Thailand is rapidly increasing, with more manufacturers discovering the domestic market.
As per the global economy, the manufacturing sector contributes to approximately 24.91% of Thailand’s GDP, making it a key aspect in the development of Thailand’s economy.
Let’s understand the various manufacturing regions of Thailand in this section:
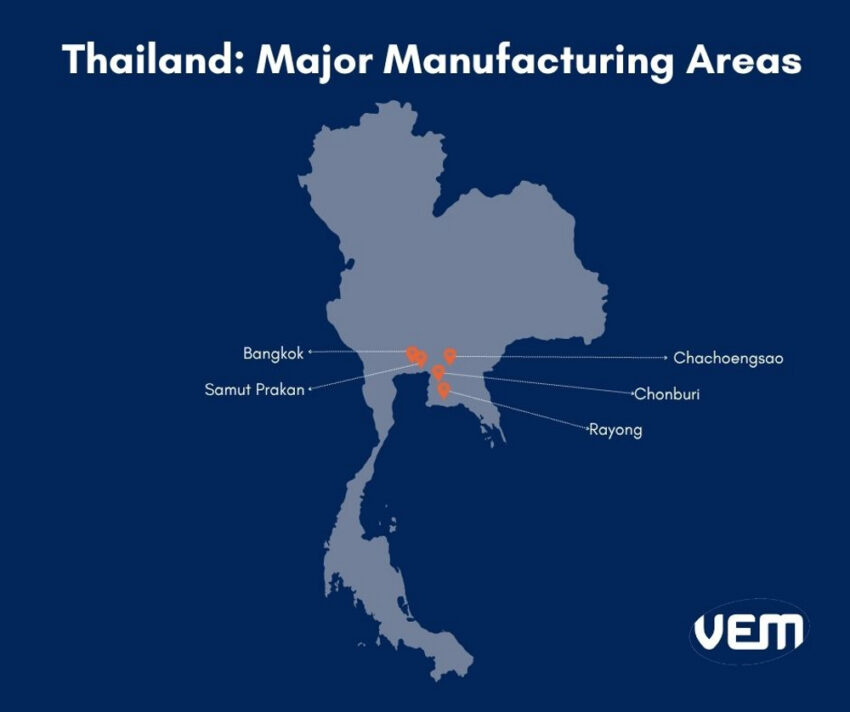
Bangkok, the capital of Thailand, is strategically located along the southern maritime border and is well-developed. Some of the major manufacturing industries within Bangkok include electronics manufacturing, textiles and garment production, food processing, and petrochemical products. The surrounding areas of Bangkok include certain automotive manufacturers.
Samut Prakan is located slightly South of Bangkok. It’s a part of the Bangkok metropolitan region and covers a large part of the southern sea border. It’s an important transportation hub. You should note that Suvarnabhumi International Airport is located here.
It has well-developed supply chains, and there are various electronics and automotive parts manufacturers here.
The Eastern Seaboard is a major industrial region. It comprises Chonburi, Rayong, and Chachoengsao provinces. The province also includes the country’s biggest seaport, Laem Chabang.
Chonburi has various electronics and automotive parts manufacturers, whereas Rayong mainly has rubber and petrochemical manufacturers. Chachoengsao province is also a major industrial region for electronics, automotives, and supporting industries.
Thailand’s eastern seaboard is a promising manufacturing hub due to its well-built infrastructure and low labor costs.
Manufacturing in Thailand serves as a strategic advantage. Let’s understand these advantages further:

Thailand is located in the central zone of Southeast Asia. Its infrastructure is well-developed, which makes it accessible through sea, air, road, and rail. Thus, Thailand’s connectivity is efficient, which makes it a strategic base for logistics and distribution. It also has several industrial estates that include well-built factories and are accessible to international ports and transportation networks.
It’s crucial to select the right manufacturing location. Thailand is well-established for providing manufacturing solutions to various industries.
Thailand has also developed EEC, a government-backed initiative. It spans three eastern provinces and has a top-tier infrastructure that is dedicated to industrial estates.
You can diversify your supply chain through Thailand as it offers political stability, a mature industrial base, and strong IP protection laws. All these factors contribute to making Thailand an excellent alternative for global manufacturers.
Thailand’s government is focused on building a skilled workforce. They have a well-established education system that supports industrial requirements, including technical and vocational training. The government regularly invests in STEM education to ensure that the labor force is aligned with the requirements of high-tech manufacturing.

Thailand is popularly known as a business-friendly nation.
In 2020, it secured 21st position in the World Bank’s EODB, abbreviated for Ease of Doing Business, among 190 countries globally. The World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business index indicates business regulations, policies, and taxes in countries. You can read about it here.
Thailand is actively promoting digitalization and automation in manufacturing under its “Thailand 4.0” economic initiative. It’s also continually evolving to include smart factory technologies, data analytics, and artificial intelligence.
Thailand is actively emphasizing green manufacturing practices and adopting renewable energy to meet the global demands of sustainable production.
The government of Thailand offers both tax and non-tax incentives through the BOI, abbreviated for the Board of Investment. These include corporate tax exemption of up to 13 years, exemptions for importing machinery and raw materials, and land ownership rights for foreign investors. In addition, BOI facilitates the visa and work permit processes for foreign employees.
It’s crucial to protect intellectual property in any business. You should note that Thailand has a robust legal framework for protecting intellectual property.
The manufactured products must be according to local and international standards. In Thailand, regulatory bodies such as TISI, abbreviated for the Thai Industrial Standards Institute, set guidelines for safety and quality. Thus, product standards are met.
The Thai government offers extremely competitive corporate tax rates. These tax rates can be further reduced if BOI incentives are applicable.
If you are seeking to manufacture high-quality plastic parts with reliability and cost-efficiency, then plastic injection molding in Thailand is a cogent option.

VEM Tooling and Medical in Thailand is a manufacturing facility that focuses on producing high-quality plastic parts for the automotive and medical industries. It’s located in Pluak Daeng District in Rayong.
VEM Thailand has an ISO 8, i.e., level 100,000 cleanroom and large capabilities for medical molding and assembly. You can view more details about VEM Tooling’s Thailand facility here, and also, book a tour with us if you are in town.

VEM Tooling’s plastic injection molding facility in Thailand is dedicated to providing you with manufacturing expertise and exemplary service. We ensure that you receive an excellent end-to-end experience.
You can contact us to further understand the benefits of manufacturing in Thailand and learn how our injection molding facility in Thailand can solve your manufacturing requirements.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.