

S7 tool steel is versatile, durable and a high-performance material. S7 steel demonstrates excellent shock resistance and belongs to the category of oil-hardening, air-hardening, non-deforming tool steels. Its unique properties enable manufacturers to employ it for a wide array of applications in various industries. It’s especially employed when shock-resistance, ease of machining and heat treatment are a priority.
In this article, we discuss the specific properties of S7 tool steel and why it is popular in manufacturing and industrial applications.
S7 is a high-carbon, low-chromium alloy, shock resisting tool steel that is characterized by its toughness and wear resistance. It combines high impact strength, good dimensional stability and machinability with excellent resistance to shock thus, making it a preferred steel of choice for various applications.
S7 tool steel is also referred to as air or oil hardening steel as it can be hardened in air or oil respectively.
AISI S7 tool steel demonstrates the highest hardenability and resistance to softening at elevated temperatures among the S-series steels. These particular properties of S7 tool steel make it popular amongst manufacturers in shock-resistant applications.
Its unique properties are what makes it popular for high-impact and high-stress applications. It’s thus employed for a wide range of tool and die applications. In addition, S7 tool steel is employed for both cold and hot work tooling applications:
The hardenability of S7 Steel and other group S steels can be changed and controlled by varying their composition. It is possible to achieve optimum hardness with S7 steels at higher austenitizing temperatures. The tempering resistance is enhanced through silicon, which forms a microstructure that resists distortion in tempered conditions. Since it demonstrates air-hardening properties, it is safe and stable to use in heat treatments.
S7 tool steel is susceptible to corrosion. It can easily rust and corrode which is why it should be kept away from moisture and humidity. During storage, it is recommended to consider using rust inhibitors and wrap it in corrosion-resistant materials such as plastic or wax paper.
S7 tool steel is of the shock-resistant tool steel family. It demonstrates excellent resistance to high shock. It thus, is an ideal application that involves high stress, shock, and impact. It also exhibits excellent toughness.
S7 tool steel demonstrates excellent wear resistance due to its high Carbon content. It is thus ideal for applications, where high levels of abrasion and wear resistance are a priority.
S7 tool steel demonstrates good dimensional stability. It thus, can maintain its shape and size even under high stress and pressure which makes it ideal for applications that require high precision and accuracy.
S7 tool steel can be applied to an array of applications. It is particularly useful in applications where resistance to high impact and shock is required. The most common applications are listed below:
S7 tool steel is a high-carbon steel. Just like other high-carbon steels, S7 tool steel decarburizes during thermal processing.
The tempering temperatures for S7 tool steel are low. Due to the low tempering temperatures, S7 tool steel is typically not suitable for nitriding or similar treatments.
S7 tool steel is machinable but comparatively, it’s more difficult to machine than the lower alloy steels. It’s difficult to machine due to its high alloy content.
S7 tool steel has various advantages but it has a distinct limitation of being less resistant to wear and tear. Comparatively, S7 tool steel is less resistant to wear and tear than other tool steels.
Mold steel is grouped and labeled by AISI, abbreviated for the American Iron and Steel Institute, and SAE, abbreviated for the Society of Automotive Engineers in the United States.
AISI and SAE have jointly developed UNS, abbreviated for Unified Numbering System. UNS is a steel grade numbering system and the UNS for S 7 Tool Steel is UNS T41907.
AISI classification system denoted the letter ‘S’ to categorize a particular set of mold steels i.e. ‘Group S’ steels. All steels that are designated with the letter S are low alloy steels and the main alloying elements in these mold steels are Chromium and Molybdenum.
The S group of steels includes mold steels such as S1, S2, S5, S6, and S7 steels.
S7 tool steel is a popular shock-resisting tool steel and it has similar grades, available internationally. These grades are not S 7 steel but similar in element and composition. It is thus crucial to comply with the country’s standards. The equivalent grades of AISI S7 tool steel in Germany and China are listed below:

S7 tool steel is a popular shock-resistant tool steel. It demonstrates excellent toughness, strength and durability.

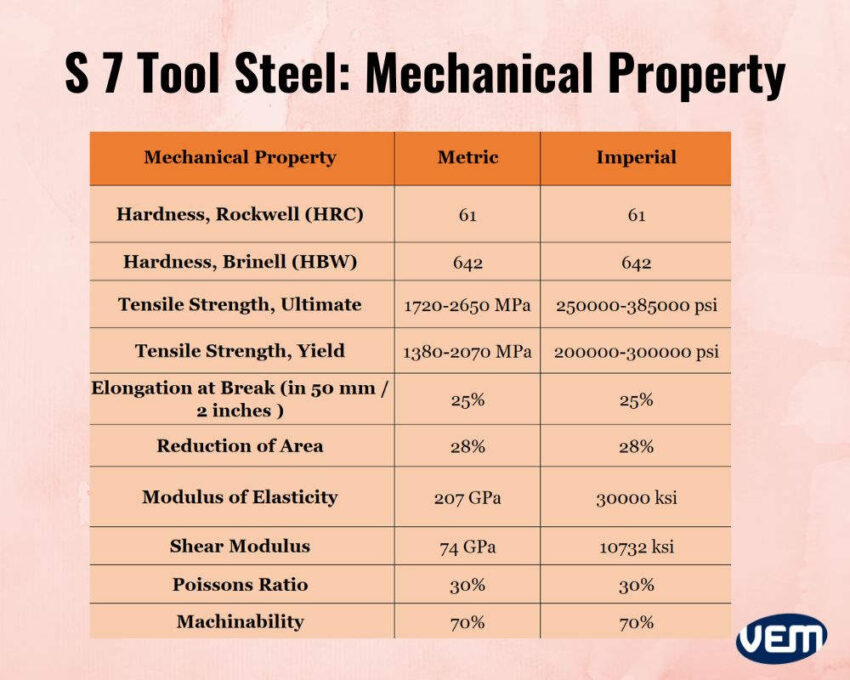
S7 tool steel demonstrates good polishability and is easily machinable. It also demonstrates excellent dimensional stability and weldability. The hardness of S7 tool steel ranges between 54-62 HRC.
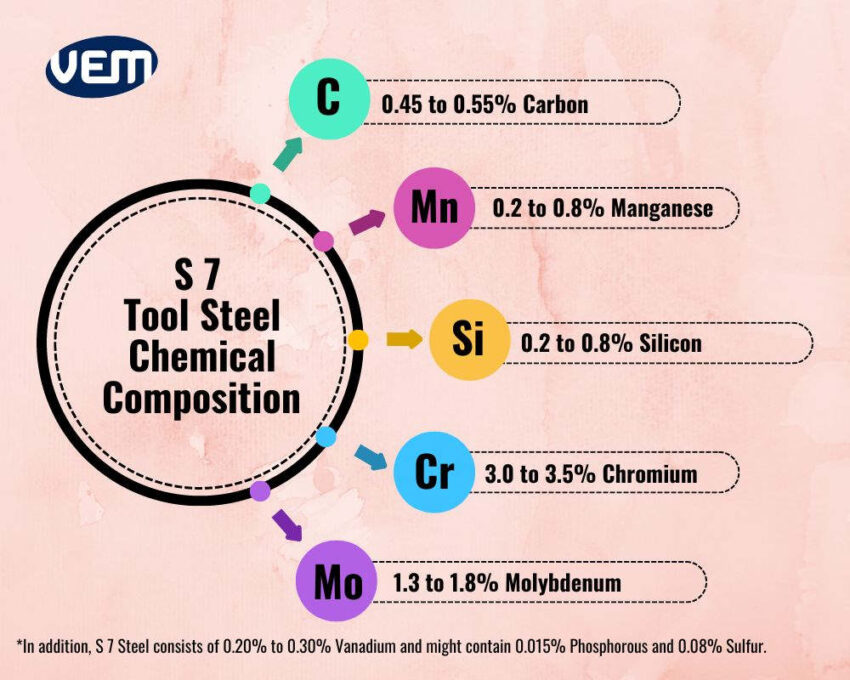
S7 tool steel is a shock-resistant tool steel. The chemical composition of AISI S 7 tool steel consists of 0.45 to 0.55% Carbon along with 3.0 to 3.5% Chromium, 1.3 to 1.8% Molybdenum, 1.2 to 0.8% Manganese, 0.2 to 0.8% Silicon, 0.2 to 0.3% Vanadium along with trace quantities of Sulfur and Phosphorous.
S7 tool steel is heated at a rate of 222°C / 400°F per hour. If the tools are complex and large, then they can be heated between 621-677°C / 1150-1250°F.
If the geometries are simpler, then only the second preheating temperature range is used.
The heat treatment of Annealing eliminates internal stresses. You should note that the annealing should occur in a protective atmosphere. During this particular heat treatment, S7 tool steel is heated rapidly to a temperature of 815-845 °C / 1500 to 1550°F and held for 1 hour for each inch of thickness / 25.4mm.
In order to attain the best machining properties, it is recommended that you cool the steel slowly to 537.7ºC / 1000°F, which is further air cooled or cooled in the furnace at 28°C / 50°F.
Austenitizing is a heat treatment process in which the steel is heated above a critical temperature to transform the microstructure of the steel. In the case of S7 steel, the steel is heated slowly from the preheat in a furnace. During austenitization, the temperature is maintained at 941°C / 1725°F in the furnace. It’s further soaked for 30 minutes for 1 inch / 25.4 mm of thickness.
S7 tool steel can be hardened by placing it in a furnace. The temperature setting is typically between 927°C – 954°C/ 1700°F – 1750°F.
Stress relieving eliminates machining stresses. It is carried out to prevent deformation. In the case of S7 tool steel, stress relieving should be carried out by heating the steel to approximately 650oºC /11732ºF for 1-2 hours. The steel is further air-cooled.
S7 can be quenched via air, pressurized gas, or warm oil. It is typically quenched at temperatures between 51°C-66°C / 125°F-150°F.
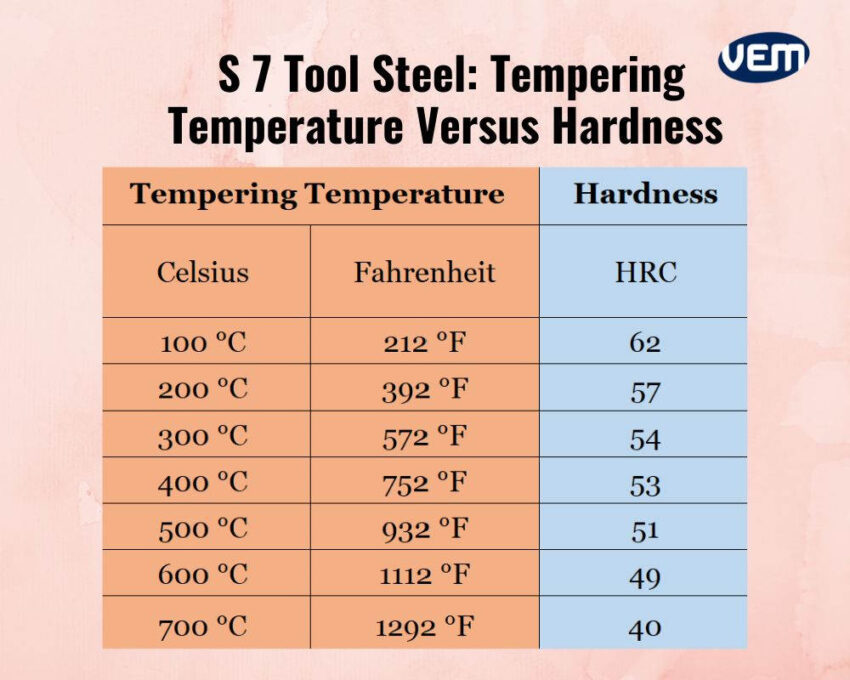
S7 tool steel is tempered immediately after quenching. The tempering temperature is dependent upon the application and is carried out to achieve the required properties. If it’s a hot work tooling application, then the tempering temperature should be between 482.22°C – 537.7 °C / 900°F-1000°F and if it’s a cold work tooling application, then the tempering temperature should be between 204°C to 260°C / 400°F to 500°F. The steel is tempered for one hour per inch/ 25.4 mm of section thickness. It’s further air cooled to room temperature.
S7 tool steel demonstrates good machinability at a rate of 70%. It is readily machineable through conventional techniques such as milling, turning, and drilling.
You should note that the hardness of S7 tool steel is high, and it is thus recommended to use apt cutting tools to achieve the required results.
Forging is carried out to shape the steel through localized forces such as pressing and hammering. S7 tool steel can be forged at a temperature of 1093°C – 1121°C / 2000°-2050°F.
S7 tool steel demonstrates moderate weldability. It’s necessary to ensure preheating and post-welding treatments are carried out correctly to avoid cracking.
It’s also recommended to incorporate suitable filler materials so that the material integrity and its properties can be maintained.
S7 tool steel is a shock-resisting steel that’s durable and versatile and suitable for a range of application in the tool manufacturing business.
VEM Tooling has a vast experience of over 20 years and our team of experts can help you with valuable recommendations. They can guide you with selecting the correct steel for your manufacturing solution.