

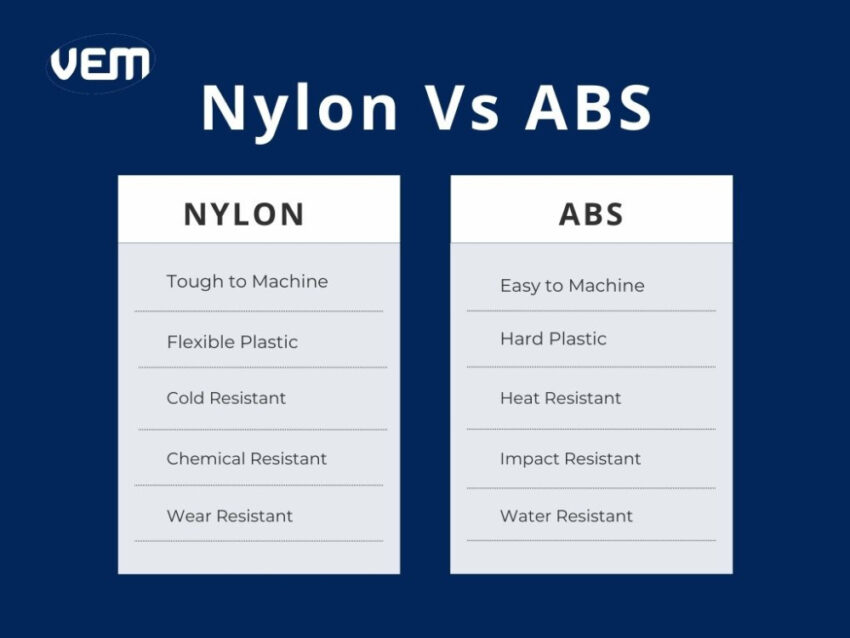
In the manufacturing landscape, there is a wide range of engineering-grade thermoplastics available for manufacturing high-quality plastic parts and creating prototypes. Among them, two of the most commonly employed materials are Nylon plastic and ABS material, both of which are applied for distinctive roles in various industries. A Nylon VS ABS is long overdue, let’s dive into the unique properties and extensive applications.
ABS material is known for its impact resistance, rigidity, and smooth finish, whereas Nylon plastic offers superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability. These differences make each material uniquely suited for specific applications. In this article, we discuss each material, compare their properties, and their application areas.
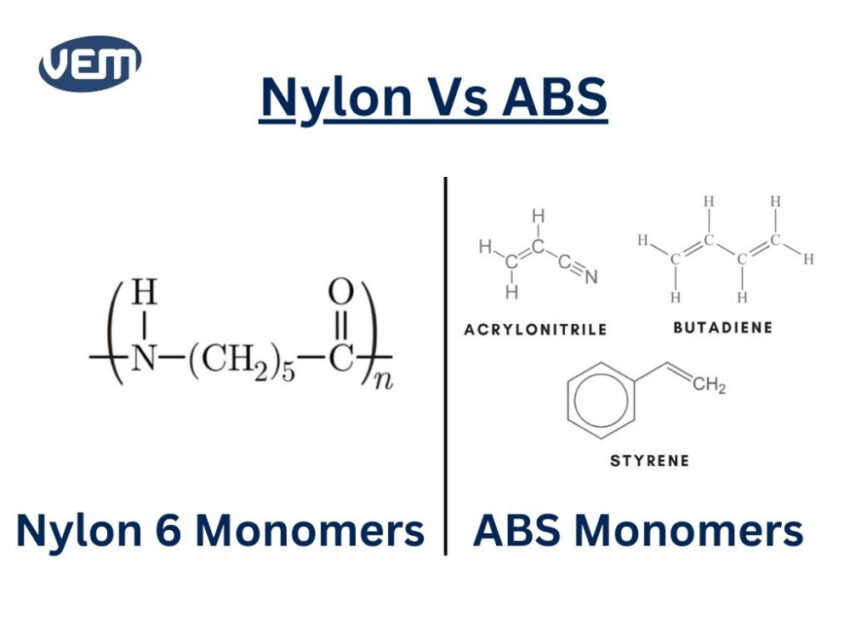
Nylon plastic is a synthetic polymer and is known for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. It’s composed of polyamide resins and is produced through the polymerization of petroleum-based ingredients.
Nylon is versatile and cost-effective. It also blends well with other fibers and can thus be enhanced to increase the durability and performance of the part. You can read more about Nylon here and glass-filled Nylon here.
Nylon plastic demonstrates a high tensile strength and resistance to impact. It can maintain its structural integrity for heavy-duty parts. It is thus apt for parts that need to endure stress and wear for a prolonged duration.
It also demonstrates excellent dimensional stability as it’s able to maintain its shape well under varying temperatures and pressures. Thus, ensuring consistent performance.
Nylon plastic demonstrates a low friction coefficient. It also demonstrates excellent wear and abrasion resistance. Thus, Nylon is apt when smooth motion for a prolonged time is crucial.
It demonstrates good strength and weight balance. It’s lightweight but can handle large mechanical loads, thus enabling overall part weight reduction.
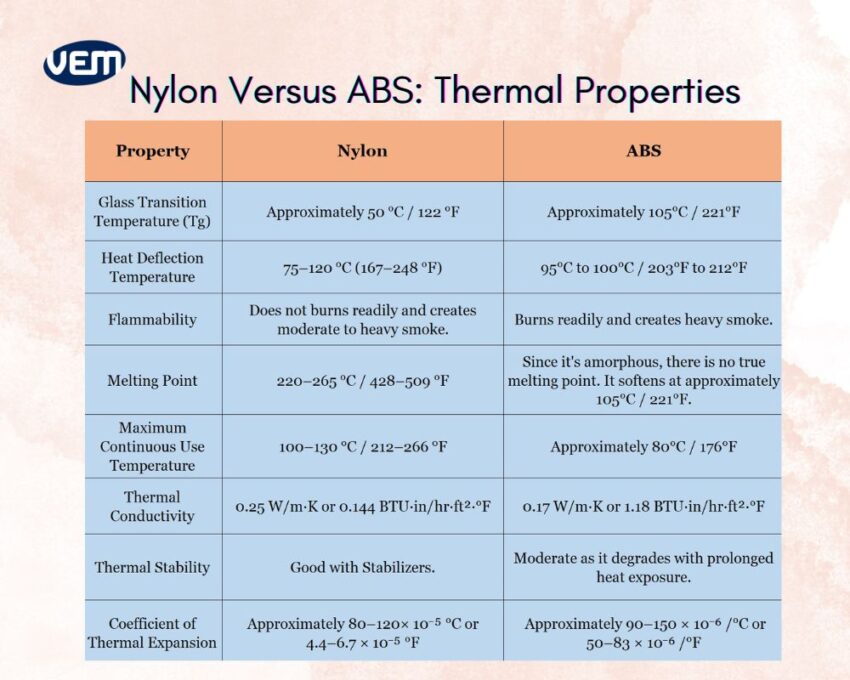
It demonstrates good thermal resistance as it has a high melting point. Thus, Nylon plastic can perform well in moderately high-temperature environments without deforming.
Nylon plastic is customizable with additives as it can be modified to enhance its properties with glass fibers, flame retardants, or UV stabilizers. Thus, it’s an extremely versatile plastic that’s adaptable to manufacturing unique and for specific requirements.
Nylon is sensitive to extreme heat and thus melts at extremely high temperatures. It’s not ideal for use near open flames or in high-heat industrial applications.
Nylon is synthetic, so it tends to generate static electricity. This can sometimes attract dust and be a hindrance in certain applications.
Nylon is petroleum-based and is non-biodegradable. It thus has an environmental impact.
ABS, abbreviated for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a versatile thermoplastic that’s known for its excellent impact resistance, smooth surface finish, and ease of processing. When compared to Nylon plastic, it molds easily at lower temperatures, making it more energy-efficient and cost-effective in mass production.
ABS material is apt for parts, where aesthetic appeal and post-processing, such as painting or plating, is a priority. You can read more about ABS here.
ABS is impact resistant as it demonstrates excellent toughness and resilience. It’s thus ideal for various heavy-duty applications.
ABS material demonstrates both rigidity and toughness. While Nylon is stronger and more abrasion-resistant, ABS offers better rigidity and is more stable under static loads.
ABS plastic demonstrates a naturally smooth, glossy surface finish. Unlike Nylon, it can be painted, plated, or printed, which is why it’s perfect for consumer goods, where aesthetics are a priority.
Just like Nylon, ABS plastic maintains its shape during molding, but it absorbs less moisture than Nylon, which gives it an edge in precision for tight-tolerance parts in humid conditions.
ABS plastic demonstrates excellent flexibility as it’s extremely ductile and malleable. It enables manufacturers to create complex and intricate designs.
ABS plastic has a lower melting point than Nylon, which makes it less suitable for high-temperature environments.
ABS plastic has a lower abrasion resistance, which is why it isn’t ideal for high-friction or moving parts.
ABS material degrades when exposed to sunlight for a prolonged duration, which demonstrates poor UV resistance. It thus needs to be UV-stabilized.
The tensile strength of ABS material is lower than that of Nylon. Since it’s less flexible, it can crack under high-stress bending.
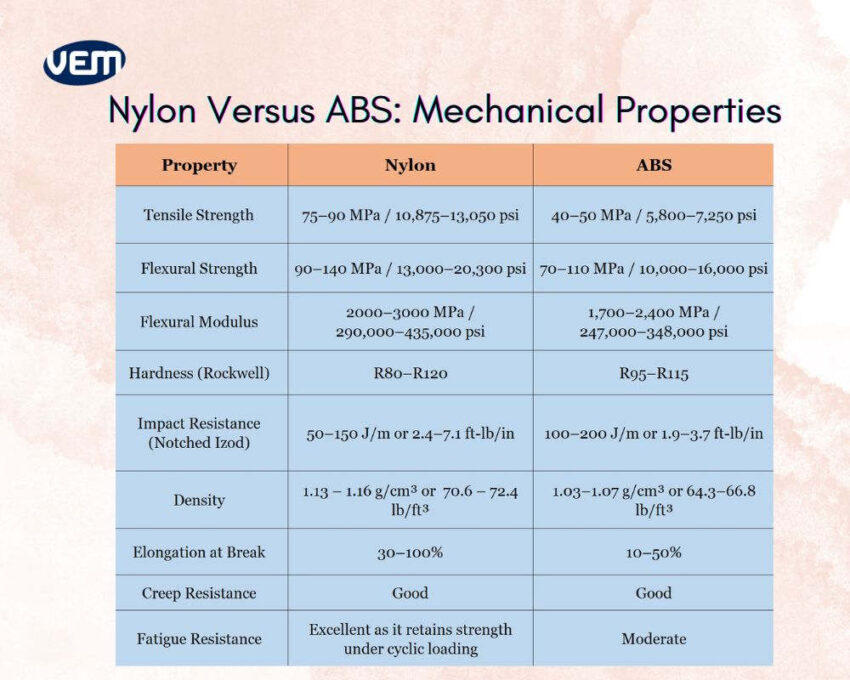
Stiffness is measured by the flexural modulus parameter. In this case, Nylon is superior to ABS plastic. Nylon’s flexural strength is also slightly higher than ABS, which indicates that it has a better capacity to withstand bending forces. It also outperforms ABS plastic in terms of tensile strength, making it better suited for load-bearing applications.
Nylon plastic demonstrates excellent fatigue resistance, which also makes Nylon apt for parts that experience repetitive stress or vibration over time.
The hardness ratings, i.e., the Rockwell scale, for both materials are quite comparable, with Nylon ranging between R80–R120, and ABS plastic ranging between R95–R115, suggesting that both materials are reasonably hard and scratch-resistant. However, ABS material has a higher impact resistance than Nylon, which is measured by Notched Izod. Thus, ABS material is apt for parts where high toughness and impact absorption are a priority.
Both materials exhibit good creep resistance, which means that they can resist long-term deformation under continuous stress. However, Nylon outperforms ABS plastic in terms of elongation at break. It’s more ductile and flexible as it can stretch significantly more than ABS plastic.
Both Nylon and ABS demonstrate poor to moderate performance towards acids. Nylon plastic, however, demonstrated good resistance except for strong oxidizing bases, whereas ABS material is moderately resistant, which makes nylon suitable for alkaline environments. In addition, Nylon also demonstrates good resistance towards solvents, particularly against aliphatic solvents. ABS, on the other hand, is easily attacked by ketones and esters.
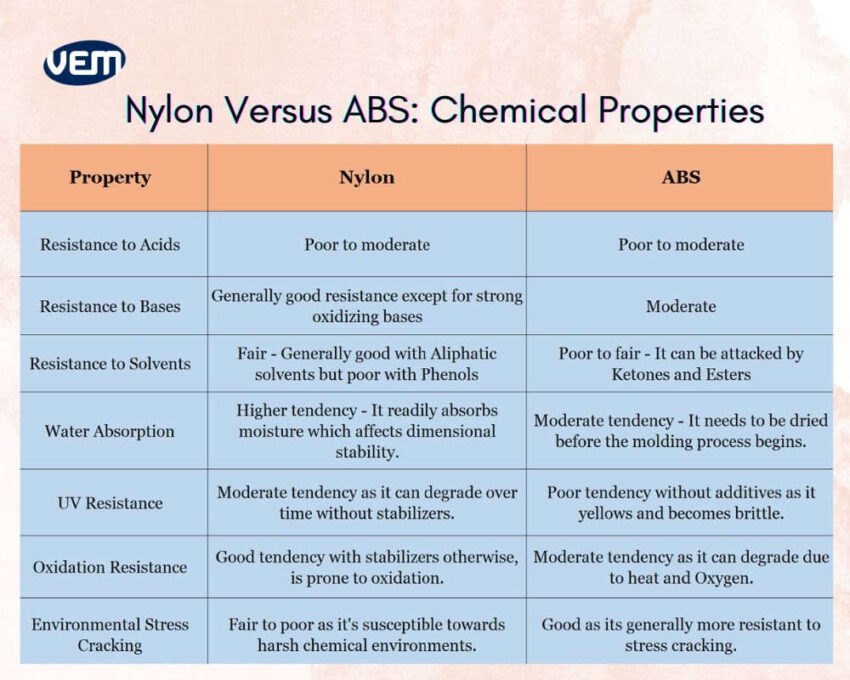
Nylon has a higher tendency to absorb moisture, which can impact its dimensional stability over time, whereas ABS material demonstrates a moderate tendency. It must be dried before molding.
In terms of UV resistance, both materials are susceptible to degradation, but to different extents, and in terms of oxidation resistance, Nylon performs well with stabilizers, whereas ABS material demonstrates moderate resistance towards oxidation. In the case of environmental stress cracking, ABS material outperforms Nylon plastic, as it is generally more resistant to stress cracking.
Nylon plastic is better suited for high-temperature applications as it has a higher melting point than ABS material. You should note that ABS, being an amorphous plastic, doesn’t melt but instead softens at around 105°C / 221°F.
Heat deflection temperature indicates how the molded parts perform under mechanical stress. Both have similar heat deflection temperatures, but PP plastic performs better under continuous heat exposure due to its semi-crystalline structure.
Thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion indicate how the material cools and shrinks within the mold. Since ABS plastic is amorphous, it cools more uniformly, thereby allowing for tighter tolerances, whereas PP plastic may need to be compensated in tool design to manage shrinkage.
Both ABS material and PP plastic have a wide range of applications in various industries. Let’s understand when ABS and Propylene are employed in some of the most popular industries in this section:
ABS material and PP plastic are widely applied in automotive applications. They are, however, chosen strategically, which is typically based on the required functions and aesthetics.

Nylon demonstrates greater resilience as its heat deflection temperature indicates that it can tolerate up to 120°C / 248°F, thus making it more ideal for prolonged exposure to higher temperatures than ABS material. This is further reinforced by the maximum continuous use temperature, which ranges for Nylon plastic between 100–130°C / 212–266°F, while ABS material is only up to 80°C / 176°F.
Thermal conductivity indicates that both materials are poor heat conductors. However, Nylon demonstrates good thermal stability with stabilizers, whereas ABS plastic tends to degrade more easily under prolonged heat exposure.
Nylon plastic and ABS material are applied in distinctively different roles within the automotive industry due to their characteristics. Nylon is widely used to manufacture interior components that require strength and durability, such as seat belt components and airbag housings. Since these components are critical for safety, they must be able to withstand significant mechanical stress and sudden impacts. Thus, Nylon is an apt material for high-stress applications due to its excellent tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and thermal stability.
In contrast to Nylon, ABS plastic is applied for parts that require a smooth finish and don’t undergo mechanical stress, such as internal door handles, HVAC vents, and dashboard trims. ABS can be easily molded into complex, aesthetic shapes, and it allows for easy color matching, which is why it’s apt for interior styling.
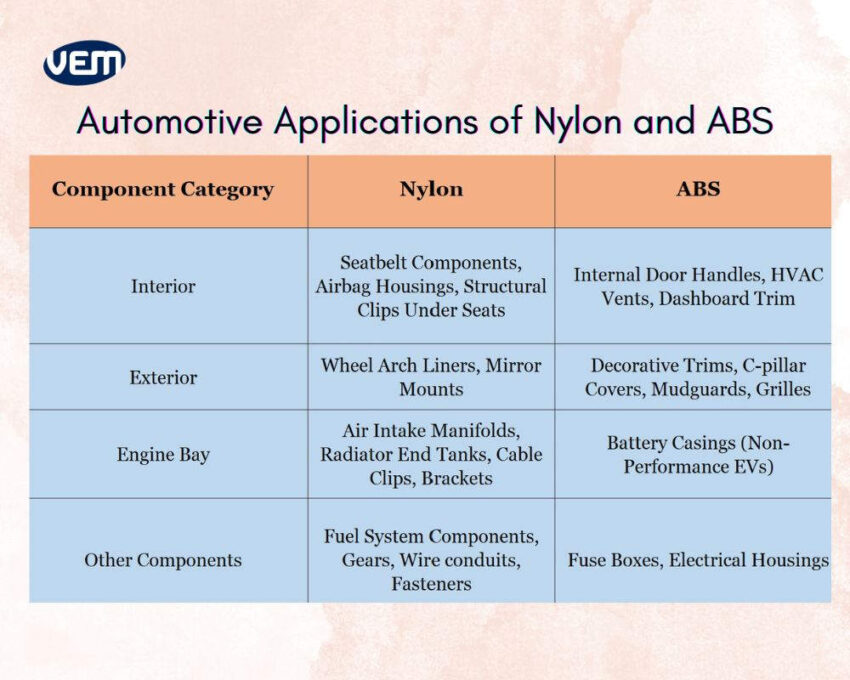
Nylon can maintain mechanical integrity under harsh conditions and, thus, in exterior applications, is applied for manufacturing structural components that undergo mechanical stress, temperature fluctuations, and continually face environmental exposure, such as grille supports, engine covers, and under-the-hood fasteners. ABS, on the other hand, is only used when weathering and impact resistance are less of a concern, such as for exterior trims or light-duty parts.
Materials are exposed to high heat, continuous vibration, and exposure to chemicals such as fuel and coolant within the engine bay. In such cases, Nylon stands out due to its exceptional thermal resistance and structural integrity, which is why it’s apt for manufacturing components such as air intake manifolds, radiator end tanks, and cable brackets. It can maintain its performance and shape under extreme operating temperatures that are found within the engine. ABS, on the other hand, is applied when the heat exposure and structural stress are minimal, such as battery casings for non-performance EVs, fuse boxes, and electrical housings.
In industrial applications, Nylon plastic is selected for high-performance mechanical roles, whereas ABS material is applied when aesthetics and lightness are a priority.
Nylon’s superior mechanical strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and fatigue make it an apt material for gears, bushings, sprockets, and washers as they undergo repetitive motion, friction, and load. Its durability and resilience also make it a preferred material for fasteners, wire insulation, and conveyor belt links where reliability under stress is a priority. ABS material, on the other hand, is applied for electrical switch housings and plug casings, where aesthetics and ease of machining are a priority.
ABS material performs well in creating lightweight structural parts. These components also benefit from ABS’s excellent moldability and surface finish, whereas Nylon plastic is particularly employed for manufacturing parts where resilience is a priority, such as machine frames and conveyor belt links.
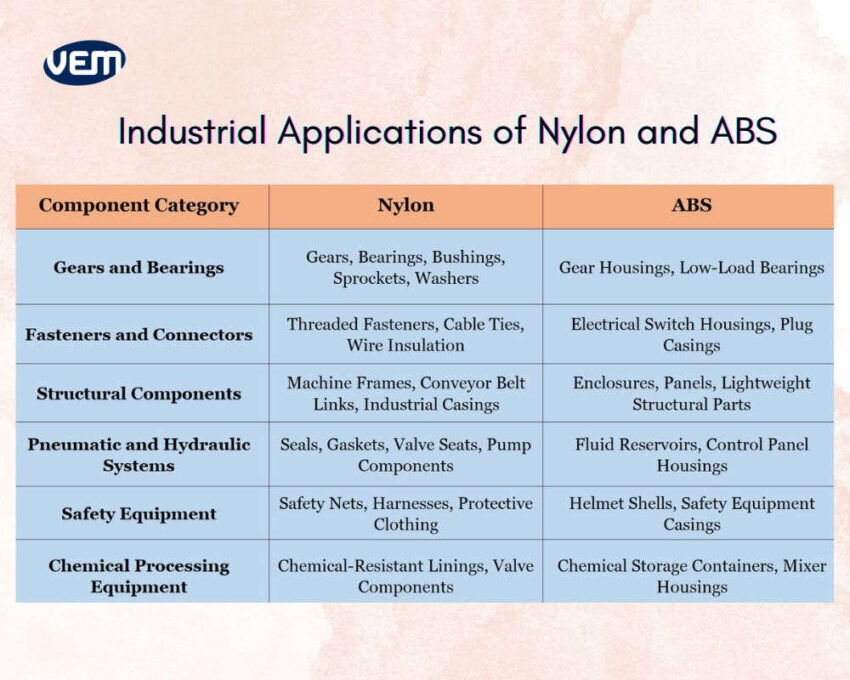
When it comes to fluid systems and chemically exposed environments, Nylon is mostly applied for manufacturing seals, valve seats, pump components, and gaskets in pneumatic and hydraulic systems due to its chemical resistance and ability to retain shape and function under pressure. ABS material is apt for fluid reservoirs and mixer housings since here, mechanical integrity is a priority.
Nylon plastic is particularly employed for performance-driven medical components, whereas ABS material is applied more in user-interfacing roles.
Nylon plastic is commonly applied for manufacturing surgical instruments and diagnostic devices where high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability are a priority, such as laparoscopic tool components and probe connectors, as they undergo frequent sterilization and mechanical stress.
ABS material, on the other hand, is preferred for lightweight, ergonomic parts that demand precision, aesthetics, and a clean finish over durability, such as disposable forceps, diagnostic tool handles, e.g., thermometers, and imaging equipment housing, e.g., ultrasound housings.
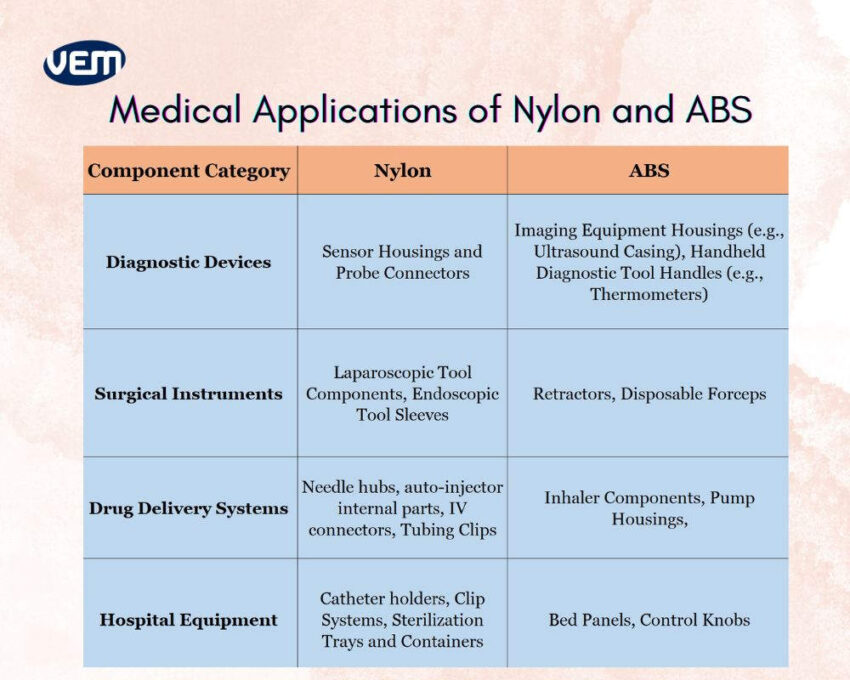
In drug delivery systems, Nylon plastic is applied, where durability, chemical inertness, and high-pressure resistance are a priority, such as needle hubs, auto-injector internals, and IV connectors, so that they maintain integrity under frequent mechanical stress and during exposure to bodily fluids. On the other hand, ABS material is applied to manufacture inhaler casings and pump housings due to its moldability, lightness, and smooth surface finish.
In hospital equipment, Nylon is employed for structural and stress-bearing parts, which require long-term durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear, such as catheter holders or clip systems. ABS, on the other hand, is employed for visually prominent, low-load parts such as hospital bed panels, monitor enclosures, and control knobs.
In the electronics sector, Nylon plastic and ABS material serve complimentary but distinct purposes, and it’s largely dependent upon whether the application demands structural performance or aesthetic finesse.
ABS material is commonly employed for manufacturing battery components such as chargers and battery pack casings, and device housings such as computer casings, television shells, and smartphone bodies due to its smooth surface finish and ease of molding into complex forms. Nylon plastic, on the other hand, is employed in manufacturing battery holders, insulating spacers, router casings, and industrial device housings as it can withstand mechanical stress.
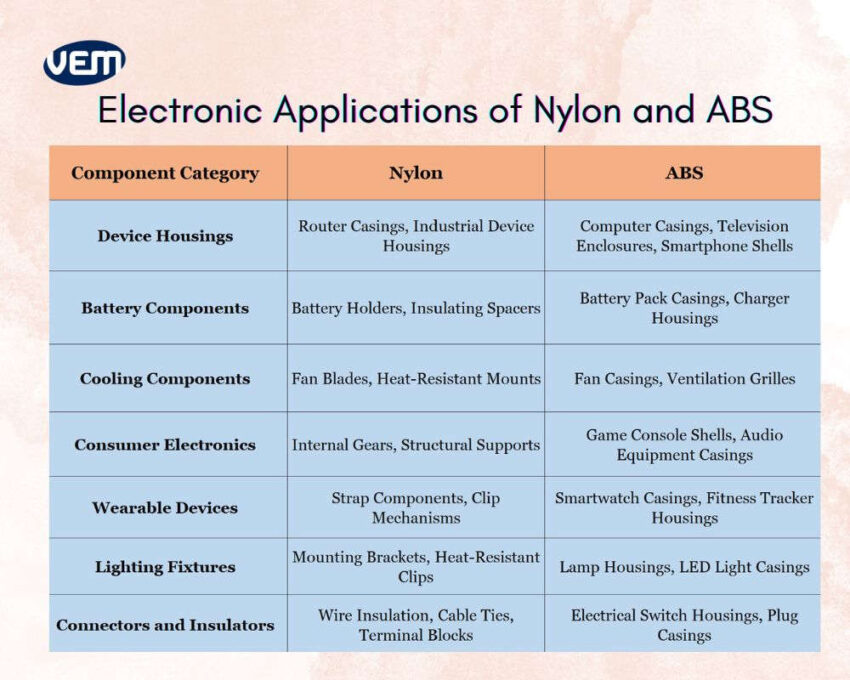
Nylon plastic is applied for various demanding mechanical roles within electronic assemblies such as fan blades and heat-resistant mounts in cooling components as it can withstand continuous motion and high temperatures without warping or degrading. ABS material, on the other hand, is applied for manufacturing external fan casings, as it doesn’t have the thermal endurance or mechanical strength to reliably perform in moving or load-bearing parts.
ABS material is applied to manufacture sleek casings in smartwatches and fitness trackers. Nylon plastic, on the other hand, is applied where flexibility and fatigue resistance are crucial such as strap components or internal structural elements.
In the case of internal components of lighting fixtures, connectors, and insulators, the most apt material is Nylon plastic due to its toughness, abrasion resistance, and durability under strain, which is why it is used to manufacture mounting brackets, cable ties, terminal blocks, and wire insulation. These components benefit from Nylon plastic, as they are constantly flexed or exposed to heat. ABS material, on the other hand, is suitable for light and plug casings, switch housings, where rigidity and form precision are needed, but the mechanical demands are relatively low.
The success of manufacturing high-quality consumer goods is through the correct and smart pairing of ABS material and Nylon plastic. ABS material is employed for user-friendly design and affordability, while Nylon is applied for performance and longevity. This enables manufacturers to create parts that are not only aesthetically pleasing but can also withstand wear and tear.
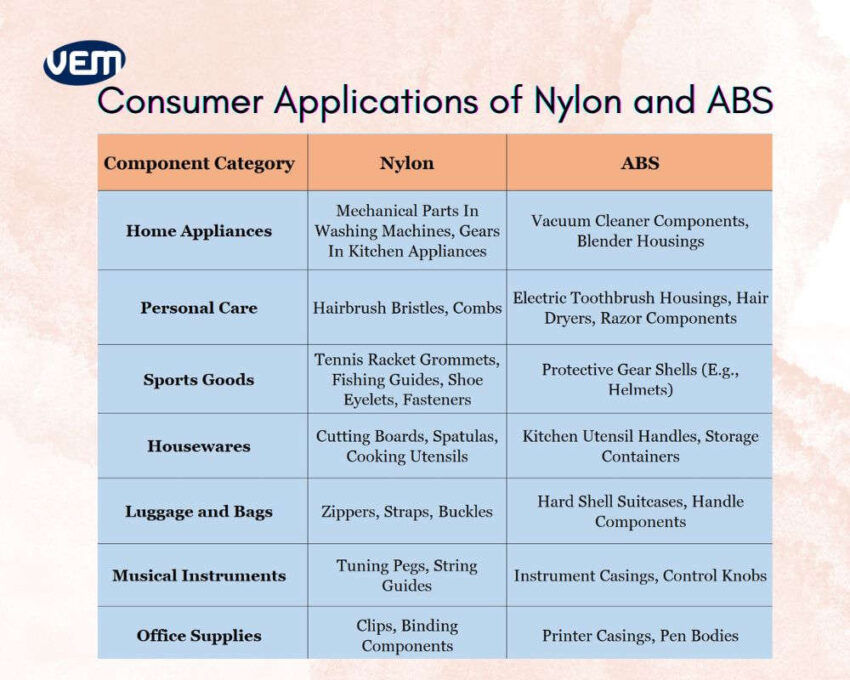
ABS material is widely applied for parts that require aesthetic appeal, lightweightness, and precision molding such as remote controls, hairdryer bodies, electric toothbrush housings, and vacuum cleaner shells. Nylon plastic, on the other hand, is typically employed for manufacturing internal, load-bearing, or high-wear components such as washing machine parts and cable organizers.
In most consumer goods, the exteriors are manufactured with ABS material and the interiors are manufactured with Nylon plastic.
Nylon and ABS are applied for distinctive roles as they have very specific applications. While some of their properties might overlap, they demonstrate unique characteristics, which is why it’s crucial to select the most apt material.
VEM-Tooling has over 20 years of experience in providing solutions for and manufacturing high-quality plastic parts. Our experienced engineers and design experts can guide you to understand which material is apt for your part and other manufacturing solutions.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.