

Tooling is at the ‘heart’ of injection molding techniques! Tooling design dictates the quality of the plastic parts produced and the efficiency of the injection molding processes. This is applicable for both, a simple design as well as a complex application.
There are various molding processes in injection molding techniques and every process has a specific type of tooling requirement. It is imperative to understand these requirements as they help to manufacture visually appealing and functionally correct plastic parts.
Two major tooling technique categories that are popularly used are soft and hard tooling. The soft tooling technique is applied for creating prototypes and small production runs whereas the hard tooling technique is applied for high-volume production runs. Another major difference between the two tooling techniques is that the material used in soft tooling is either Silicone or Carbon fiber whereas the material used for hard tooling techniques is either Steel or Aluminum. In this article, we discuss the differences between soft and hard tooling and the use cases for these techniques.
Two major tooling technique categories that are popularly used are soft and hard tooling. The soft tooling technique is applied for creating prototypes and small production runs whereas the hard tooling technique is applied for high-volume production runs. Another major difference between the two tooling techniques is that the material used in soft tooling is either Silicone or Carbon fiber whereas the material used for hard tooling techniques is either Steel or Aluminum. In this article, we discuss the differences between soft and hard tooling and the use cases for these techniques.
Before we get into soft and hard tooling techniques, let’s first understand what exactly is ‘tooling’. Tooling is integral to injection molding and is one of the critical aspects of the manufacturing process. Tooling is also known as machine tooling. In manufacturing, we need tooling for our tool designing and development.
Tooling is a project investment and needs to be designed correctly, in order to meet the part specification requirements. If the tool design is not correct or according to the part specifications, then the requirements will not be met which will result in making more modifications. These modifications will consume more time and increase the costs of the overall project. Tooling is a highly technical and complex process that requires expertise and experience to produce high-quality parts.
If the tool is designed faulty, then it can cause complications and errors in manufacturing. Thus, it is imperative that the tooling process is accurately designed.
It is also critical that the right tooling process is implemented for your project. Choosing the right tooling process not only ensures that you achieve the highest quality product but also ensures that you do so within purpose, schedule, and budget. It is thus important to note the nuances and understand the differences between soft and hard tooling techniques.
The molds for the soft tooling techniques are usually made with silicone, carbon fiber, or fiberglass, and each mold cavity can carry out 25–50 shots. One of the most commonly used soft tooling materials is silicone which is why this tooling method is also referred to as silicone tooling but you should note that soft tooling molds can be made from other materials as well.
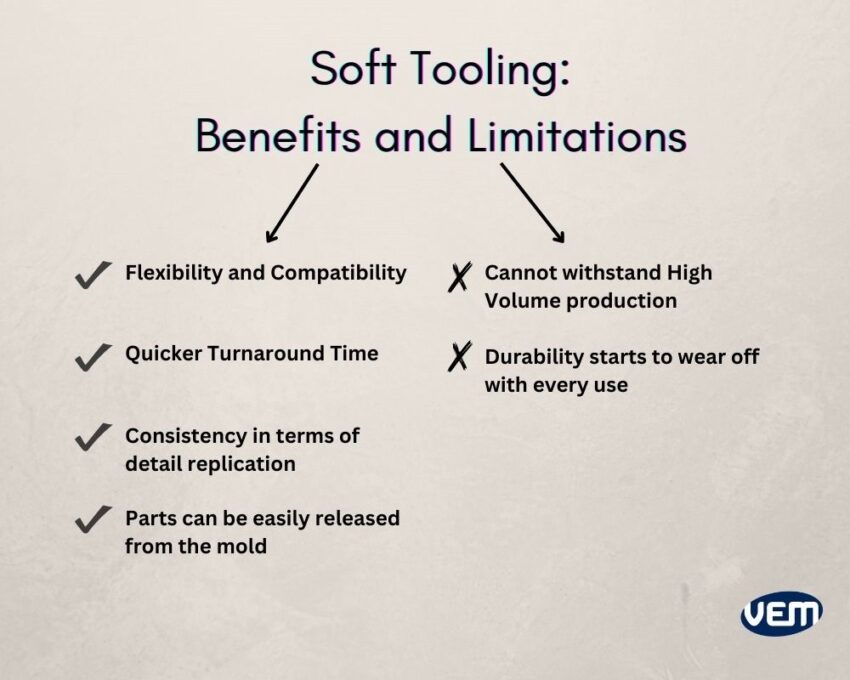
Soft tooling is applied for manufacturing prototypes and producing parts in low-volume that typically ranges between 1 to 100 parts. This tooling technique is ideal for manufacturing simple functional parts. It can be used to produce complex mold patterns but there are certain limitations. Depending upon the part geometry, the silicone tooling cost can be anywhere between hundred to thousands of dollars but they are still, comparatively cost-effective.
Most manufacturers choose soft tooling because it’s comparatively cheaper and flexible for low-volume runs. If the design is altered and a new tooling requirement arises, it can be done so at a low cost.
Soft tooling creation begins with a master pattern. The surface finish of this pattern is critical as the surface directly translates from the master pattern to the material. Optimal soft tool creation that includes the required feature details and surface finish is carried out through additive manufacturing techniques like Stereolithography and PolyJet 3D printing. The master patterns need to undergo finishing before the tool creation. Once the master pattern is complete, the soft tooling material is cured. After curing, the master pattern is removed, and the soft tooling material is cast to make the mold.
A tube manually feeds these molds with the materials and depending upon the type of material used, it can take anywhere between 1 to 24 hours for the parts to cure. When the parts cure, the molds are opened. The mold opening is done manually after which, the surface finishing may be carried out.
Hard tooling techniques are very distinct in terms of their process and use case than soft tooling techniques. Hard tooling is more expensive and time-consuming. It also takes more time to build hard tools as they need to undergo heat treatment and post-processing.
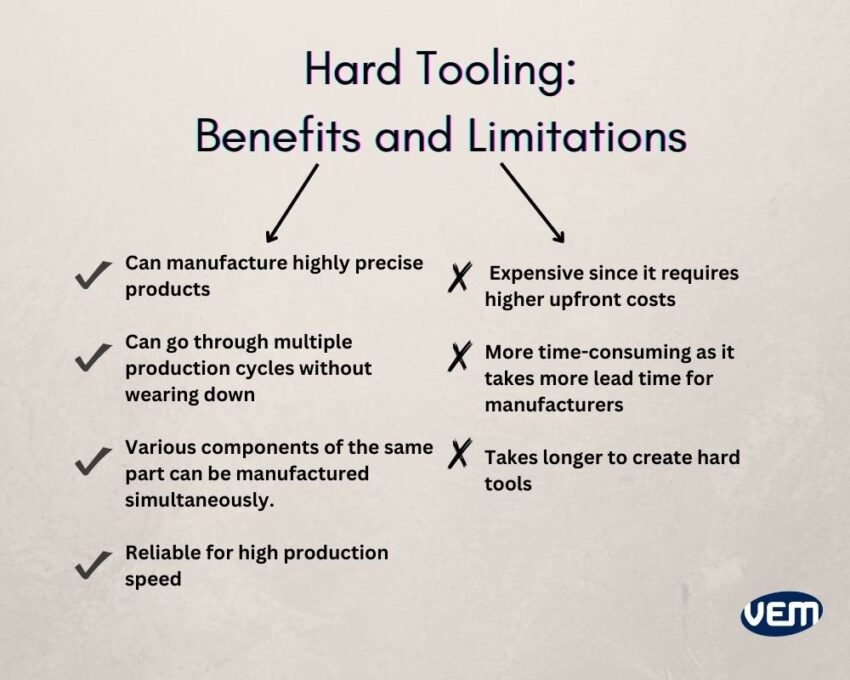
The molds for hard tooling techniques are made from tough metals such as varying grades of Steel, Aluminium, and Nickel alloys. Hard tooling is especially used to produce plastic parts in high volumes and it can withstand several production cycles. The life of hard tools is comparatively and significantly long and can go up to millions of parts.
Soft steel and Aluminum are used for manufacturing prototypes and low production runs such as 100 -10,000 parts. Depending upon the steel quality, larger production run volumes such as 1,000,000 – 2,000,000 shots can be achieved. The lifetime of the mold can also be increased with good maintenance and if the material used is non-abrasive.

Depending upon the geometry and the type of material used, hard tools are also more expensive and they can cost anywhere from thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
In hard tooling, studier materials are used to make the molds. To make hard tooling molds, parts are built using hardened steel dies. These are known as ‘tools’ and they are set up in heavy tonnage stamping presses. In the case of hard tooling, multiple features such as cuts and bends can be formed simultaneously in the stamping press.
To create the required shape, often, multiple press operations are needed. After the tool is formed as per the requirements, the production is carried out through plastic injection molding.
Molten plastic is injected from an injection mold machine. During injection molding, the plastic pellets are first melted and once they are in a molten state or are sufficiently malleable, they are injected into the mold cavity. At this stage, high pressure is applied.
Molding material then solidifies within the mold and the curing occurs within seconds to minutes. Since the hard tooling process does not take much manpower and it cures within minutes, it’s quicker to yield more parts.
Hard tooling is majorly used for high-volume production runs. Since they can withstand multiple production cycles and are reproducible in terms of accuracy and precision, they are applied to manufacture simple and complex parts by an array of industries. Hard tooling can be used to manufacture plastic parts in various industries that range from the consumer, automotive, and aerospace to the medical and healthcare industry.
Soft tooling is an ideal option if speed, flexibility, and affordability are your priorities but if this is not a priority and you need high-volume production, then hard tooling is ideal. Let’s understand the differences between the tooling techniques:
Tooling Material: Soft tool molds are built using softer materials such as Silicone and Carbon fiber whereas hard tool molds are built using hard materials such as Steel, Aluminium, and Nickel.
Molding Volume: Soft molds are ideal for low-volume quantities of 1 to 100 parts whereas hard molds can support huge volume production runs of 100 to 1,000,000 parts.
Cost Efficiency: This factor largely depends upon the geometry and complexity but soft tooling is comparatively more cost-effective than hard tools.
Production Efficiency: Hard tooling is less labor intensive than soft tooling as in this case the machine injects the molten material into the mold which takes less manpower. Hard tooling also yields parts faster than soft tooling.

If soft tooling should be chosen for speed, flexibility, and affordability then, hard tooling allows for better features and challenging requirements in plastic parts.
Both the techniques have their pros and cons. The decision of choosing between soft and hard tooling should be based on the project requirements. Let’s understand the various aspects that one should look into for choosing between the 2 types of tooling techniques:
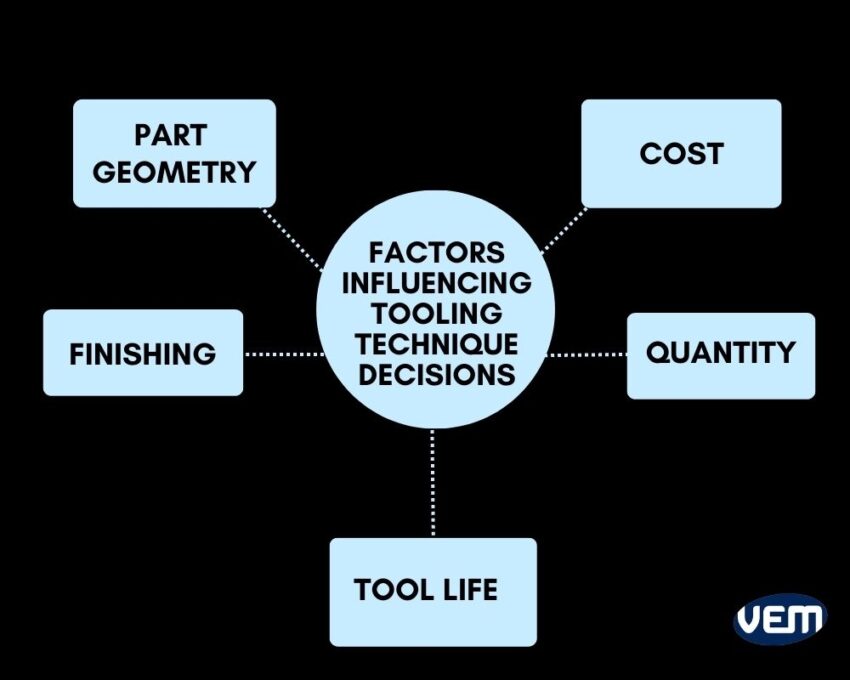
If the geometry is complex, it is recommended to choose soft tooling as this technique has quicker turnaround times and is more cost-effective. If there is a redesign needed, it is easier to do so with soft tooling techniques as they use 3D printing and CNC machining which can produce complex soft tools within hours to days. After the design has been perfected, it can be progressed to hard tooling.
If you want your tools to have a prolonged lifespan, then soft tooling shouldn’t be your choice. As discussed earlier, soft tools don’t last for a very long time and they are efficient only for 25-50 shots. On the other hand, hard tools are more sustainable and they can be used for thousands of shots. The reason is that hard tools can withstand high temperatures and several severe conditions.
Cost and quantity play a crucial role in determining and choosing the technique. If a manufacturer has a limited budget, and small quantity requirements, then they can go for soft tooling whereas if the manufacturer has a large quantity requirement and the budget is not a hindrance, then they should opt for hard tooling.
Finishing is the next criterion that plays a determining role in choosing the tooling method. If smoother surfaces are required, then soft over hard tooling is recommended.
There are certain time constraints with hard tooling. Hard mold tools take longer to finish than soft tools. A hard tool may take several weeks to complete, whereas a soft mold can be ready within days. You should also note that hard molds may take more time and they may be more expensive but they are much more durable and long-lasting.
Soft tools are also created before moving to hard tooling to meet market deadlines. They can be used to test the market for customer input.
Creating high-quality plastic parts needs a strong understanding of the tooling process and when it comes to tooling, an in-depth evaluation is a must! If tool types and mold processes are mismatched, then the result will be inferior plastic parts.
We help customers to bring their designs and ideas into reality. Our goal is to help our customers to produce high-quality parts with efficiency and accuracy! We have a team of engineers that have vast and in-depth experience in injection molding and tooling services. If you would like to learn more about soft and hard tooling, contact us and we will get back to you right away.